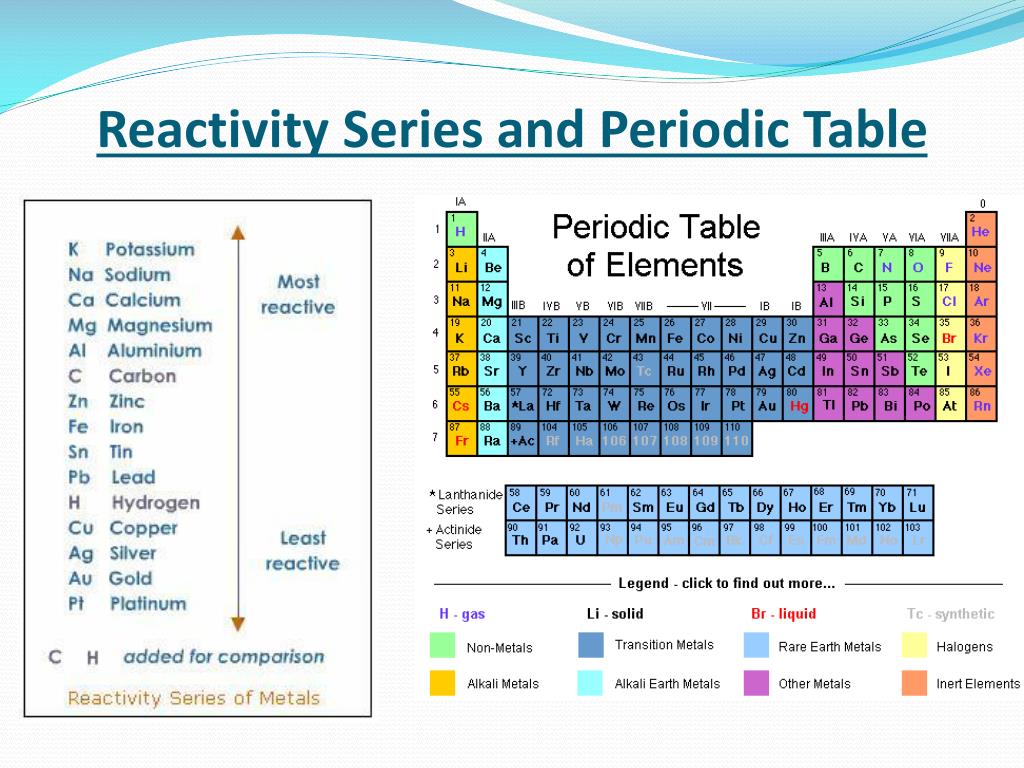
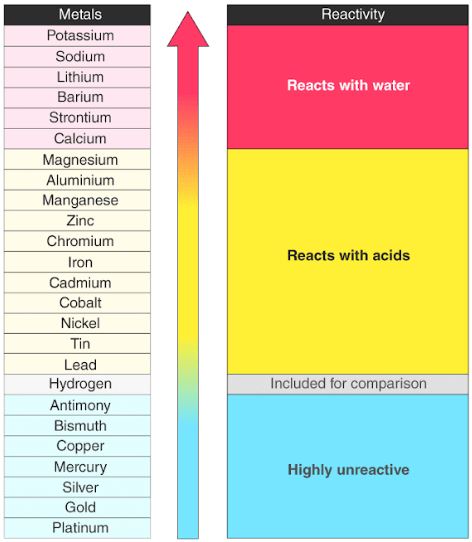
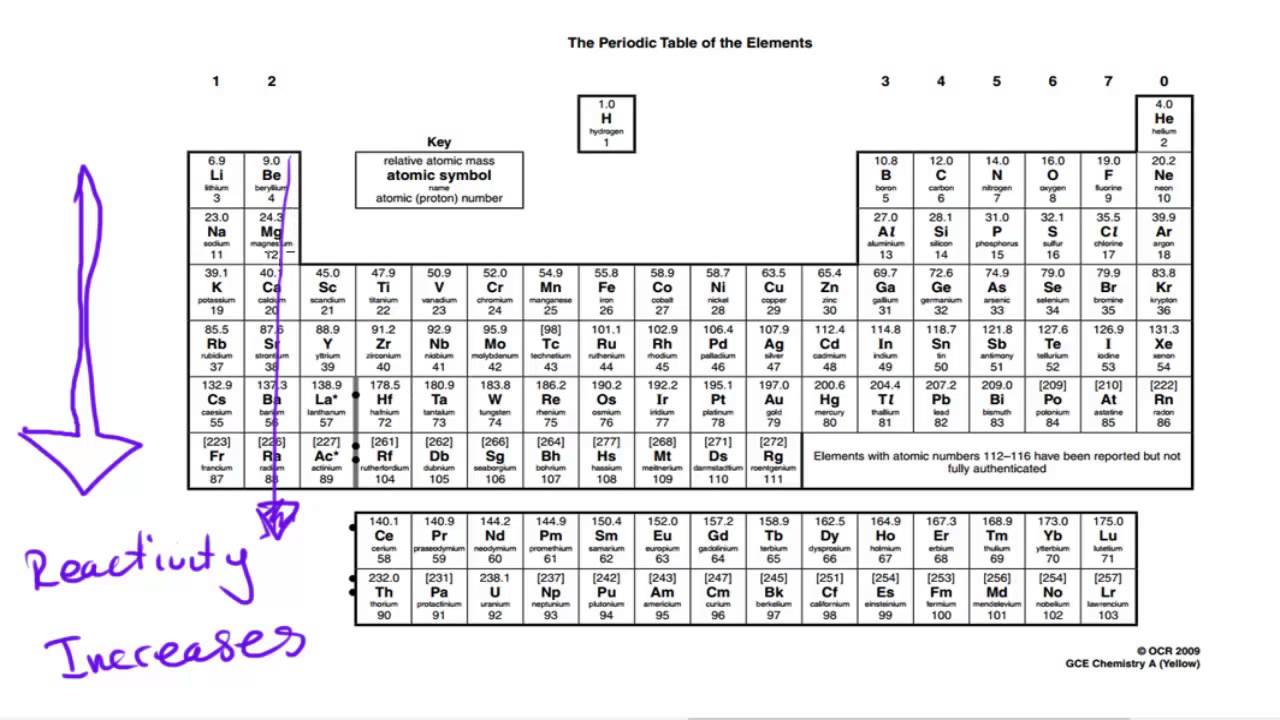
The Periodic Table In 2025: A New Era Of Reactivity Trends
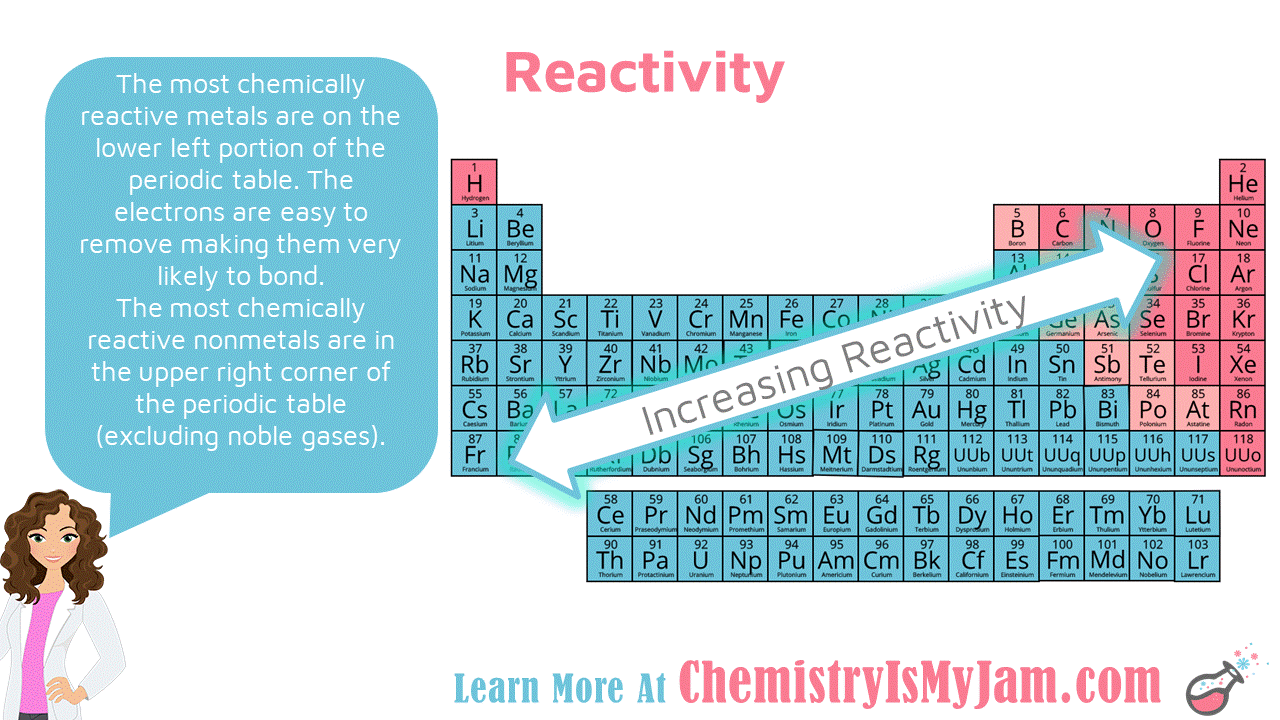
The Periodic Table in 2025: A New Era of Reactivity Trends
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, continues to evolve in its applications and our understanding of its underlying principles. As we move towards 2025, new technologies and advancements in computational chemistry are shedding light on the intricate dance of elements and their reactivity. This article delves into the evolving landscape of periodic table reactivity trends, exploring how these trends are shaping the future of materials science, medicine, and energy production.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Nuances of Reactivity
The periodic table’s familiar organization, with elements grouped by their shared properties, provides a fundamental framework for understanding chemical behavior. However, the simple notion of "metals are reactive, nonmetals are not" is a gross oversimplification. The reality is much more nuanced, with reactivity influenced by a complex interplay of factors:
- Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons within an atom dictates its tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons, driving its chemical behavior.
- Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom provides insight into its propensity to form positive ions.
- Electron Affinity: The energy change associated with adding an electron to an atom reveals its tendency to form negative ions.
- Electronegativity: The relative ability of an atom to attract electrons in a bond determines the nature of the bond formed and the overall reactivity of the molecule.
- Atomic Size: The size of an atom influences its ability to interact with other atoms, impacting the strength and type of bonds formed.
Computational Chemistry: A Powerful Tool for Predicting Reactivity
The advent of high-performance computing has revolutionized our ability to study chemical reactions at a molecular level. Quantum chemistry calculations, based on the principles of quantum mechanics, allow us to simulate and predict the behavior of molecules, including their reactivity. These simulations provide invaluable insights into:
- Reaction Mechanisms: Understanding the step-by-step process of chemical reactions, including the formation of intermediates and transition states.
- Reaction Rates: Predicting the speed at which reactions occur, allowing for optimization of reaction conditions and catalyst design.
- Product Formation: Predicting the specific products formed in a reaction, enabling the design of targeted synthesis routes.
Emerging Trends in Reactivity: A Look Ahead
The application of computational chemistry and advanced experimental techniques is uncovering exciting new trends in reactivity:
1. The Rise of Main Group Chemistry:
The main group elements, located in groups 1-2 and 13-18 of the periodic table, are traditionally considered less reactive than transition metals. However, recent research is revealing a vast potential for these elements in diverse applications:
- Novel Catalysts: Main group elements, like boron, aluminum, and phosphorus, are showing promise as catalysts for various organic reactions, offering cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional metal-based catalysts.
- Advanced Materials: Main group elements are being used to create new materials with unique properties, such as high-performance polymers, semiconductors, and luminescent materials.
- Biomedicine: Main group elements are finding applications in drug delivery systems and bioimaging, thanks to their biocompatibility and tunable properties.
2. Beyond the Periodic Table: Exploring the Exotica
The periodic table is not a static entity. The discovery of new elements, like the superheavy elements, is expanding our understanding of chemical behavior:
- Superheavy Elements: These elements, with atomic numbers greater than 103, are pushing the boundaries of our understanding of chemical bonding and reactivity. The study of their properties is challenging due to their short half-lives but holds immense potential for revealing new insights into nuclear physics and chemistry.
- Exotic Matter: Exploring the reactivity of exotic matter, such as antimatter and dark matter, could revolutionize our understanding of the universe and its fundamental forces.
3. The Importance of Environment:
The environment plays a crucial role in shaping reactivity. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of other molecules can significantly influence the outcome of chemical reactions. This understanding is leading to:
- Green Chemistry: Designing chemical processes that minimize environmental impact by utilizing renewable resources, reducing waste, and minimizing the use of hazardous materials.
- Catalysis under Extreme Conditions: Developing catalysts that function under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and pressures, is crucial for unlocking new chemical transformations and energy production methods.
4. The Role of Machine Learning:
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to analyze and predict chemical data, leading to:
- Accelerated Discovery: Machine learning can analyze vast datasets of chemical reactions and identify patterns that could lead to the discovery of new catalysts, materials, and drugs.
- Personalized Medicine: Machine learning can be used to predict the reactivity of drugs within an individual’s body, leading to personalized treatment regimens and improved drug efficacy.
Applications of Reactivity Trends: Shaping the Future
The evolving understanding of reactivity trends is impacting various fields:
1. Materials Science:
- Next-Generation Batteries: Understanding the reactivity of lithium, sodium, and other alkali metals is crucial for developing high-capacity, long-lasting batteries for electric vehicles and energy storage.
- Advanced Composites: Combining the reactivity of different elements, such as carbon, silicon, and boron, is leading to the development of lightweight and durable materials for aerospace, automotive, and construction applications.
- Nanomaterials: The reactivity of nanoparticles is being harnessed to create materials with unique optical, electronic, and catalytic properties for applications ranging from electronics to medicine.
2. Medicine:
- Drug Development: Understanding the reactivity of molecules is essential for designing drugs that specifically target disease-related proteins and pathways.
- Targeted Therapy: Using the reactivity of nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells or other diseased tissues is revolutionizing cancer treatment and other therapeutic approaches.
- Biomaterials: Understanding the reactivity of biocompatible materials is crucial for developing implants, prosthetics, and other medical devices that seamlessly integrate with the human body.
3. Energy Production:
- Renewable Energy: Harnessing the reactivity of elements like silicon, hydrogen, and oxygen is essential for developing solar cells, fuel cells, and other renewable energy technologies.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Understanding the reactivity of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases is crucial for developing technologies to capture and store them, mitigating climate change.
- Nuclear Fusion: Unlocking the potential of nuclear fusion as a clean and sustainable energy source requires a deep understanding of the reactivity of hydrogen isotopes and other elements at extreme temperatures and pressures.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the significant progress in understanding reactivity trends, challenges remain:
- Complexity of Chemical Systems: Predicting the behavior of complex chemical systems, such as those found in biological processes, remains a major challenge.
- Computational Power: Simulating complex chemical reactions requires immense computational power, which is still a bottleneck for many applications.
- Experimental Verification: Computational predictions need to be validated through experimental verification, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
These challenges also present opportunities for further innovation:
- Development of More Powerful Computing Platforms: Advances in quantum computing and artificial intelligence could revolutionize our ability to simulate complex chemical systems.
- Development of New Experimental Techniques: Developing new experimental techniques, such as ultrafast spectroscopy and high-throughput screening, can accelerate the discovery and optimization of new materials and reactions.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Close collaboration between chemists, physicists, materials scientists, and computer scientists is essential for tackling the complex challenges in reactivity research.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Reactivity Research
As we look towards 2025 and beyond, the study of reactivity trends holds immense promise for addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges, from developing sustainable energy sources to curing diseases. By harnessing the power of computational chemistry, advanced experimental techniques, and interdisciplinary collaboration, we can unlock the full potential of the periodic table and create a brighter future for humanity.