The Future Is Now: Trends Shaping 2025-2026

The Future is Now: Trends Shaping 2025-2026
The world is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, societal shifts, and global events. As we stand at the precipice of 2025, the landscape of trends is already shaping the future, influencing everything from our daily lives to global economies. This article delves into the key trends that will dominate 2025-2026, exploring their implications and potential impact.
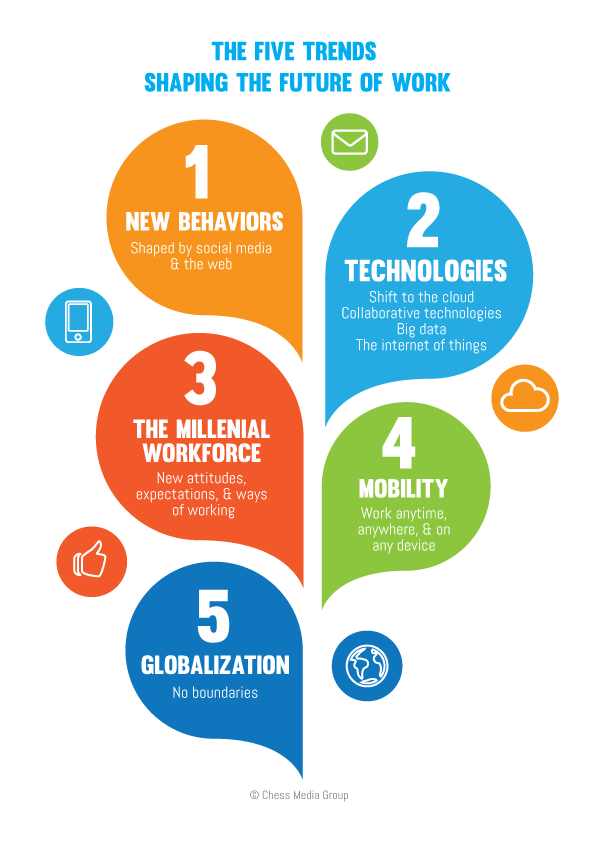
1. The Rise of the Metaverse and Web 3.0:
The metaverse, a persistent, shared virtual world, is no longer a futuristic concept but a rapidly developing reality. 2025-2026 will witness the mainstream adoption of immersive technologies like VR and AR, transforming how we work, socialize, and consume entertainment. This will be driven by the convergence of Web 3.0, a decentralized web built on blockchain technology, empowering users with greater control over their data and digital identities.
Implications:
- Workforce Transformation: Remote work will evolve, with virtual offices and collaborative spaces becoming commonplace in the metaverse.
- E-commerce Revolution: Shopping experiences will become more immersive, allowing virtual try-ons and personalized recommendations.
- Entertainment Redefined: Immersive gaming, virtual concerts, and interactive storytelling will become mainstream entertainment forms.
- Social Interaction Reimagined: The metaverse will provide new avenues for socializing, fostering global communities and virtual friendships.
Challenges:
- Accessibility and Inclusion: Ensuring equitable access to metaverse technologies for all socioeconomic groups.
- Data Privacy and Security: Addressing the potential risks of data breaches and misuse in a decentralized environment.
- Ethical Considerations: Navigating the ethical implications of virtual identities, ownership of digital assets, and potential addiction.
2. Sustainable Living and Circular Economy:
Climate change and resource scarcity are pressing concerns, driving a shift towards sustainable living and a circular economy. Consumers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products and services, pushing businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
Implications:
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Consumers will prioritize eco-conscious brands and products, favoring sustainable materials and ethical sourcing.
- Innovation in Green Technologies: Advancements in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and circular economy models will accelerate.
- Government Regulations and Incentives: Governments will implement policies to encourage sustainable practices and penalize environmental damage.
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Businesses will prioritize environmental responsibility, adopting sustainable practices and reporting on their environmental impact.
Challenges:
- Cost and Affordability: Making sustainable options accessible to all income levels.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in sustainable infrastructure and technologies at a global scale.
- Consumer Education: Raising awareness about the importance of sustainable practices and responsible consumption.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
AI and machine learning are rapidly advancing, automating tasks, improving decision-making, and revolutionizing industries. From healthcare to finance, AI is transforming how we live and work.
Implications:
- Healthcare Advancements: AI-powered diagnostics, personalized treatments, and drug discovery will revolutionize healthcare.
- Financial Services Innovation: AI-driven risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice will enhance financial services.
- Automation and Efficiency: AI will automate repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and productivity across industries.
- Personalized Experiences: AI will personalize user experiences, tailoring recommendations, content, and services to individual preferences.
Challenges:
- Job Displacement: Addressing the potential job losses caused by automation and AI adoption.
- Bias and Fairness: Ensuring that AI algorithms are unbiased and fair, avoiding discrimination and perpetuating social inequalities.
- Ethical Considerations: Navigating the ethical implications of AI-powered decision-making, particularly in areas like healthcare and law enforcement.
4. The Future of Work and Gig Economy:
The future of work is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing societal values. The gig economy, characterized by flexible work arrangements and freelance opportunities, is growing in popularity.
Implications:
- Rise of Remote Work: Remote work will become more prevalent, fueled by technological advancements and changing employee preferences.
- Skills Gap and Reskilling: The demand for specialized skills will increase, requiring individuals to adapt and upskill to remain competitive.
- Freelancing and Gig Economy: The gig economy will continue to grow, offering flexible work opportunities and entrepreneurial freedom.
- Work-Life Balance: Flexible work arrangements will enable individuals to achieve a better work-life balance and prioritize personal well-being.
Challenges:
- Job Security and Benefits: Ensuring adequate job security and benefits for gig workers.
- Regulation and Labor Rights: Addressing the need for regulations and protections for workers in the gig economy.
- Skills Development and Training: Providing access to education and training programs to help workers adapt to the changing demands of the workforce.
5. The Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi):
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is disrupting traditional financial systems by leveraging blockchain technology to offer open, transparent, and accessible financial services.
Implications:
- Financial Inclusion: DeFi platforms can provide access to financial services for underserved populations, including those without traditional banking accounts.
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures transparency and immutability, fostering trust and accountability in financial transactions.
- New Financial Products and Services: DeFi offers innovative financial products and services, such as decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading.
- Empowerment of Individuals: DeFi empowers individuals to take control of their finances, reducing reliance on centralized institutions.
Challenges:
- Regulation and Security: Establishing clear regulatory frameworks and addressing security concerns in the DeFi ecosystem.
- Scalability and Accessibility: Ensuring scalability and accessibility for DeFi platforms to meet the growing demand.
- User Education and Adoption: Educating users about DeFi concepts and facilitating broader adoption.
6. The Importance of Mental Health and Wellbeing:
In a fast-paced and interconnected world, mental health and wellbeing are becoming increasingly important. Individuals are seeking ways to manage stress, promote mindfulness, and prioritize their mental well-being.
Implications:
- Increased Awareness and Destigmatization: Mental health awareness and destigmatization are growing, encouraging people to seek help and support.
- Focus on Mindfulness and Self-Care: Individuals are adopting mindfulness practices, seeking therapy, and prioritizing self-care to manage stress and improve mental well-being.
- Workplace Wellness Programs: Companies are implementing workplace wellness programs to support employee mental health and promote a healthy work environment.
- Technological Solutions: Apps and digital tools are emerging to provide mental health support, therapy, and mindfulness exercises.
Challenges:
- Access to Mental Health Services: Ensuring access to affordable and accessible mental health services for all.
- Addressing Stigma and Discrimination: Combating stigma and discrimination surrounding mental health issues.
- Integrating Mental Health into Healthcare: Integrating mental health care into mainstream healthcare systems to provide comprehensive support.
7. The Power of Data and Data Ethics:
Data is becoming increasingly valuable, driving innovation and shaping decision-making across industries. The responsible use of data and the ethical implications of data collection and analysis are crucial considerations.
Implications:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data analytics and machine learning are transforming decision-making in business, government, and healthcare.
- Personalization and Customization: Data is used to personalize user experiences, tailor recommendations, and offer customized services.
- Innovation and Research: Data fuels innovation and research, enabling advancements in fields like medicine, artificial intelligence, and climate science.
Challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting user data from breaches and misuse.
- Data Bias and Fairness: Addressing biases in data sets and algorithms to ensure fairness and equity in data-driven decision-making.
- Ethical Use of Data: Establishing ethical guidelines for the collection, use, and sharing of data.
8. The Rise of the Creator Economy:
The creator economy, where individuals create and monetize content online, is booming. Platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Twitch are empowering creators to build audiences, share their passions, and earn a living.
Implications:
- Shifting Power Dynamics: Creators are gaining greater influence and control over their content and audience engagement.
- New Avenues for Income: The creator economy offers alternative income streams for individuals, particularly for those seeking flexible work arrangements.
- Empowerment and Innovation: Creators are driving innovation and creativity, pushing boundaries and challenging traditional media models.
Challenges:
- Competition and Monetization: The creator economy is highly competitive, making it challenging for creators to build a sustainable income.
- Platform Dependence: Creators are often dependent on platforms for audience reach and monetization, raising concerns about platform control and potential censorship.
- Content Moderation and Ethical Considerations: Addressing issues of content moderation, misinformation, and ethical considerations in the creator economy.
9. The Future of Education and Lifelong Learning:
Education is undergoing a transformation, driven by technological advancements and the evolving demands of the workforce. Lifelong learning is becoming increasingly important as individuals need to adapt to rapidly changing skills requirements.
Implications:
- Personalized Learning Experiences: Technology enables personalized learning experiences, tailoring education to individual needs and learning styles.
- Online Learning and MOOCs: Online learning platforms and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) are expanding access to education and providing flexible learning options.
- Upskilling and Reskilling Programs: Companies and educational institutions are offering upskilling and reskilling programs to equip individuals with the skills needed for the future of work.
Challenges:
- Equity and Access: Ensuring equitable access to quality education for all, regardless of socioeconomic background.
- Teacher Training and Development: Supporting teachers in adapting to new technologies and pedagogical approaches.
- Bridging the Digital Divide: Addressing the digital divide to ensure access to technology and online learning resources for all students.
10. The Importance of Community and Connection:
In an increasingly digital world, the importance of community and human connection is growing. People are seeking meaningful relationships, social support, and a sense of belonging.
Implications:
- Community Building and Engagement: Individuals are joining online communities and participating in local events to foster connections and build relationships.
- Focus on Social Impact: Individuals are seeking to make a positive impact on their communities and the world through volunteering, activism, and social entrepreneurship.
- The Power of Empathy and Compassion: Empathy and compassion are becoming increasingly important values, fostering understanding and connection in a diverse and interconnected world.
Challenges:
- Combating Social Isolation: Addressing the increasing problem of social isolation and loneliness, particularly among older adults and marginalized communities.
- Building Trust and Collaboration: Building trust and fostering collaboration among diverse communities to address shared challenges.
- Promoting Inclusive and Equitable Communities: Creating inclusive and equitable communities that value diversity and respect for all.
Conclusion:
The trends shaping 2025-2026 are ushering in a new era of technological advancement, societal change, and global interconnectedness. From the rise of the metaverse and Web 3.0 to the growing importance of sustainability, mental health, and community, these trends are shaping how we live, work, and interact with the world.
Navigating this complex landscape requires a forward-thinking approach, embracing innovation while addressing the challenges and ethical considerations that arise. By understanding and adapting to these trends, we can unlock new opportunities, create a more sustainable and equitable future, and foster a world where technology and human connection work in harmony.