The Economic Landscape Of 2025: Navigating The Crossroads Of Innovation And Disruption

The Economic Landscape of 2025: Navigating the Crossroads of Innovation and Disruption
The year 2025 is fast approaching, and with it comes a wave of technological advancements, societal shifts, and economic uncertainties. As we stand on the cusp of this new era, it’s crucial to understand the forces shaping the economic landscape and the opportunities and challenges they present. This article will delve into key trends shaping the global economy in 2025, exploring their implications for businesses, governments, and individuals alike.
1. The Rise of the Digital Economy:
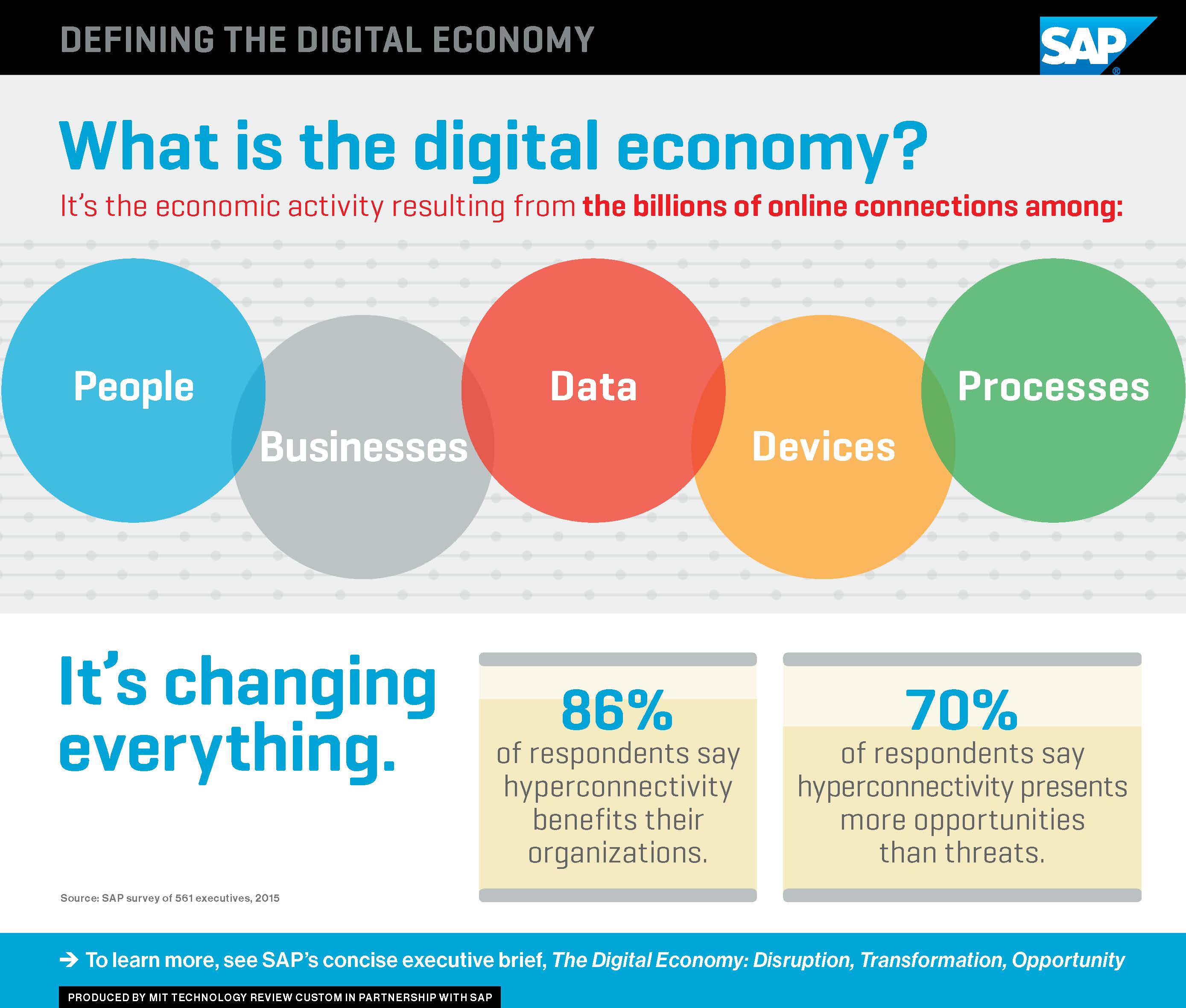
The digital revolution has already transformed countless industries, and its impact will only intensify in the coming years. By 2025, the digital economy will be a driving force, fueled by:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is poised to revolutionize industries from manufacturing to healthcare, automating tasks, improving efficiency, and creating new products and services. This will lead to increased productivity and job creation in fields like data science, AI development, and AI-related services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The interconnectedness of devices will enable real-time data collection and analysis, leading to smarter cities, optimized supply chains, and personalized consumer experiences. This will create opportunities for businesses in areas like sensor technology, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
- Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based services will continue, offering businesses greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This will create demand for cloud computing professionals, data center operators, and cybersecurity experts.
Challenges:
- Digital Divide: The benefits of the digital economy are not evenly distributed, with some individuals and regions lagging behind in access and skills. Bridging this gap will be crucial for equitable growth.
- Job Displacement: Automation and AI are likely to displace certain jobs, requiring workers to adapt and reskill for new roles. This will necessitate robust education and training programs to support the workforce transition.
- Data Security and Privacy: As data becomes increasingly valuable, protecting it from cyber threats and ensuring privacy will be paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures and data privacy regulations will be essential.
2. The Green Transition:
Climate change is a pressing global concern, driving a shift towards sustainable practices and a green economy. This transition will be driven by:
- Renewable Energy: The demand for renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro will continue to grow, creating opportunities in renewable energy production, storage, and distribution.
- Circular Economy: Businesses are increasingly adopting circular economy principles, reducing waste, reusing materials, and extending the lifespan of products. This will lead to new markets for recycling, repair, and remanufacturing.
- Sustainable Consumption: Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, driving demand for eco-friendly products and services. This will encourage businesses to adopt sustainable practices and innovate in areas like green transportation, sustainable agriculture, and eco-tourism.
Challenges:
- Cost of Transition: Shifting to a green economy requires significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure, sustainable technologies, and research and development. This can be challenging for governments and businesses with limited resources.
- Policy Uncertainty: The lack of clear and consistent policies can create uncertainty for businesses investing in green technologies. Strong policy frameworks are crucial to guide the transition.
- Consumer Behavior: Changing consumer behavior towards sustainable products and services requires education, awareness, and incentives.
3. The Rise of the Gig Economy:
The gig economy, characterized by freelance work and short-term contracts, is rapidly expanding. This trend is driven by:
- Flexibility and Autonomy: The gig economy offers workers flexibility and autonomy, allowing them to set their own schedules and work from anywhere. This appeals to individuals seeking greater control over their work-life balance.
- Technological Advancements: Online platforms and mobile technologies have made it easier for workers to connect with clients and manage their gigs.
- Shifting Workforce Demographics: Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to embrace the gig economy, seeking alternative employment models that offer flexibility and personal fulfillment.
Challenges:
- Job Security and Benefits: Gig workers often lack traditional employment benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave. This raises concerns about job security and financial stability.
- Regulation and Taxation: The gig economy presents challenges for governments in terms of regulation, taxation, and social safety nets. Clear policies are needed to ensure fair treatment and protect workers’ rights.
- Competition and Price Pressure: The gig economy is highly competitive, with workers often facing pressure to lower prices to secure gigs. This can lead to exploitation and unsustainable working conditions.
4. The Reshaping of Global Trade:
The global trade landscape is undergoing significant shifts, driven by:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Trade wars and protectionist policies are creating uncertainty and disrupting global supply chains. This is leading businesses to diversify their operations and explore new markets.
- Rise of Regional Trade Blocs: Regional trade agreements like the European Union and the Trans-Pacific Partnership are gaining prominence, creating opportunities for businesses within these blocs.
- Digital Trade: The rise of e-commerce and digital platforms is facilitating cross-border trade, creating new opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Challenges:
- Protectionism and Trade Barriers: Protectionist policies and trade barriers can hinder businesses from accessing new markets and increase costs.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Geopolitical tensions and natural disasters can disrupt global supply chains, creating challenges for businesses relying on international trade.
- Digital Trade Regulations: The lack of clear and consistent regulations for digital trade can create challenges for businesses operating across borders.
5. The Importance of Skills and Education:
The rapid pace of technological advancements and changing economic landscape highlight the importance of skills and education. Businesses and individuals need to adapt and upskill to remain competitive:
- STEM Skills: The demand for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) skills will continue to grow, particularly in fields like data science, AI, and software development.
- Soft Skills: The ability to communicate effectively, collaborate, and solve problems creatively are becoming increasingly important in the workplace.
- Lifelong Learning: The need for continuous learning and upskilling will be crucial to remain competitive and adapt to changing job demands.
Challenges:
- Skills Gap: The mismatch between the skills required by employers and the skills possessed by the workforce is a major challenge. Bridging this gap requires investment in education and training programs.
- Access to Education: Ensuring equitable access to quality education for all is essential for a skilled and competitive workforce.
- Adapting to Changing Job Demands: Individuals need to be adaptable and willing to learn new skills throughout their careers to remain relevant in a rapidly changing job market.
Conclusion:
The economic landscape of 2025 will be shaped by a complex interplay of technological advancements, societal shifts, and global trends. Navigating this evolving landscape requires businesses, governments, and individuals to embrace innovation, adapt to change, and prioritize skills development.
- Businesses: Embrace digital technologies, invest in sustainability, adapt to changing consumer preferences, and prioritize talent development.
- Governments: Promote innovation and entrepreneurship, invest in education and training, foster a skilled workforce, and create a regulatory environment that supports economic growth and sustainability.
- Individuals: Develop in-demand skills, embrace lifelong learning, adapt to changing job demands, and consider alternative employment models.
The future of the economy is not predetermined. By understanding the key trends shaping the economic landscape, we can navigate the challenges and seize the opportunities that lie ahead. This requires a collective effort to foster innovation, promote sustainability, and empower individuals to thrive in a rapidly changing world.