Navigating The Uncharted Waters: Interest Rate Trends In 2025

Navigating the Uncharted Waters: Interest Rate Trends in 2025
The year 2025 looms on the horizon, shrouded in the uncertainty that is intrinsic to economic forecasting. However, one thing is certain: interest rates will play a pivotal role in shaping the global economic landscape. Understanding the potential trends in interest rates in 2025 requires navigating a complex web of factors, including inflation, economic growth, geopolitical tensions, and central bank policies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of these factors, shedding light on the potential trajectory of interest rates in 2025 and their implications for businesses, investors, and individuals alike.
The Global Inflationary Landscape: A Persistent Challenge
Inflation has emerged as a defining feature of the global economic landscape in recent years. Driven by supply chain disruptions, pent-up consumer demand, and robust government stimulus packages, inflation has surged to multi-decade highs in many countries. While some analysts anticipate a gradual decline in inflation in 2025, others believe that persistent inflationary pressures, fueled by geopolitical tensions and structural changes in the global economy, could keep inflation elevated for longer.
Central Banks: Balancing Act Between Inflation and Growth
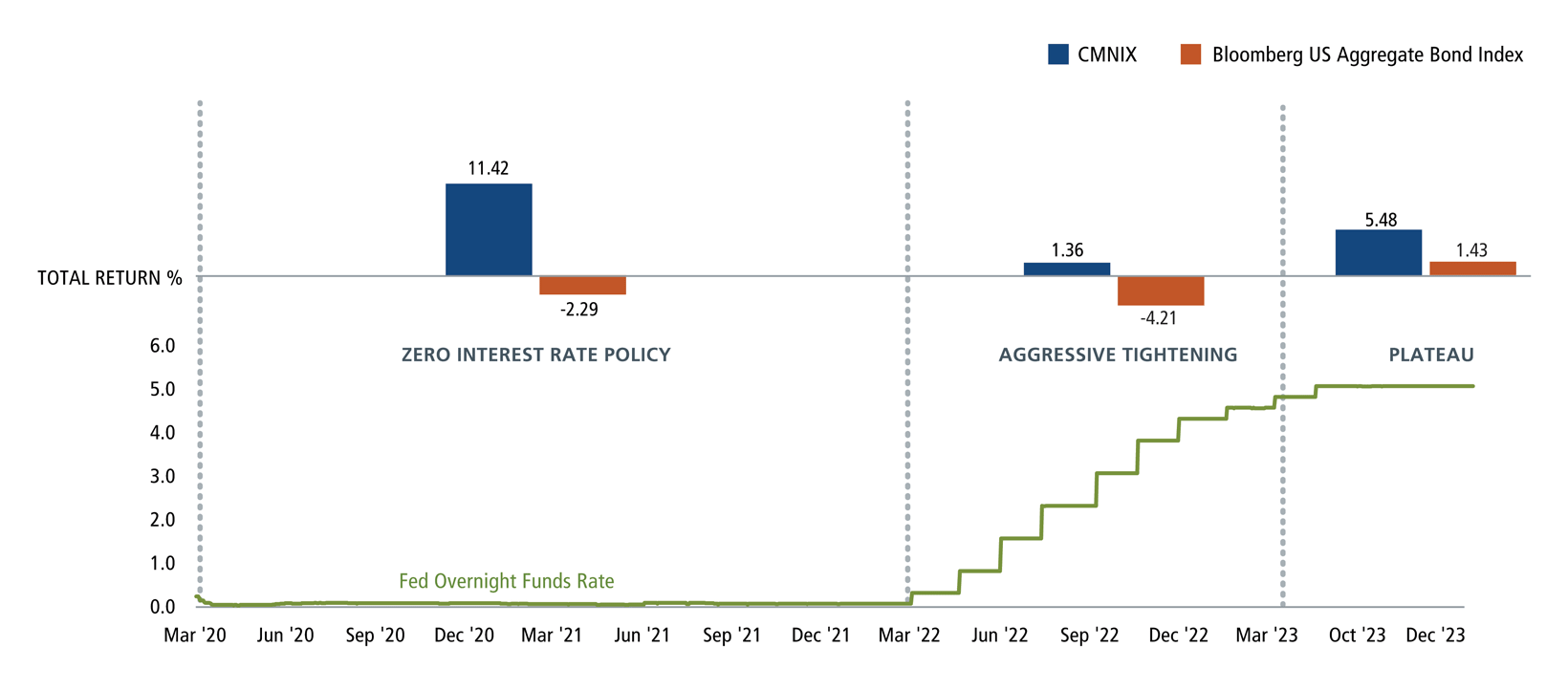
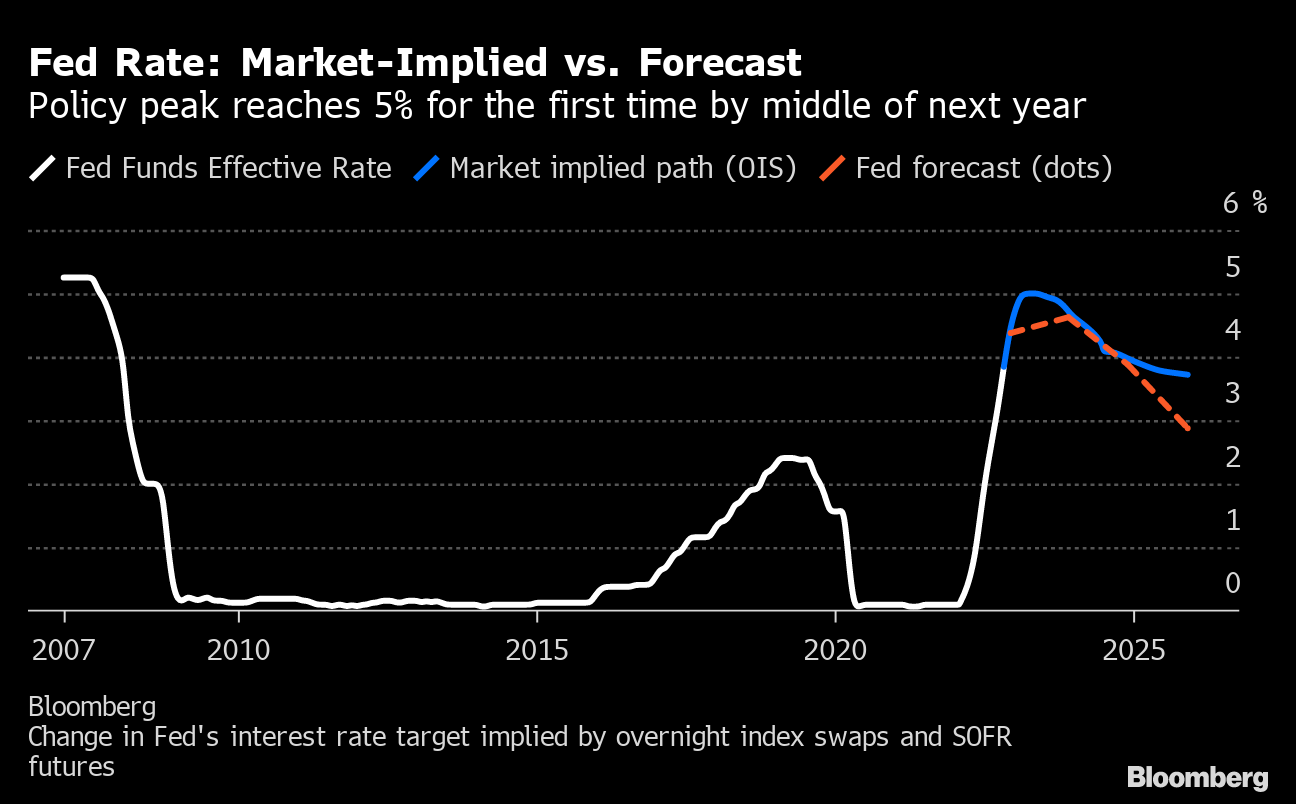
Central banks around the world have embarked on a path of aggressive interest rate hikes in an attempt to tame inflation. The US Federal Reserve, the European Central Bank, and other major central banks have raised interest rates at a rapid pace, signaling their commitment to restoring price stability. However, this tightening cycle comes with its own set of challenges. Raising interest rates too aggressively could stifle economic growth and potentially trigger a recession. The delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth will remain a key challenge for central banks in 2025.
Geopolitical Tensions: A Shadow Over the Global Economy
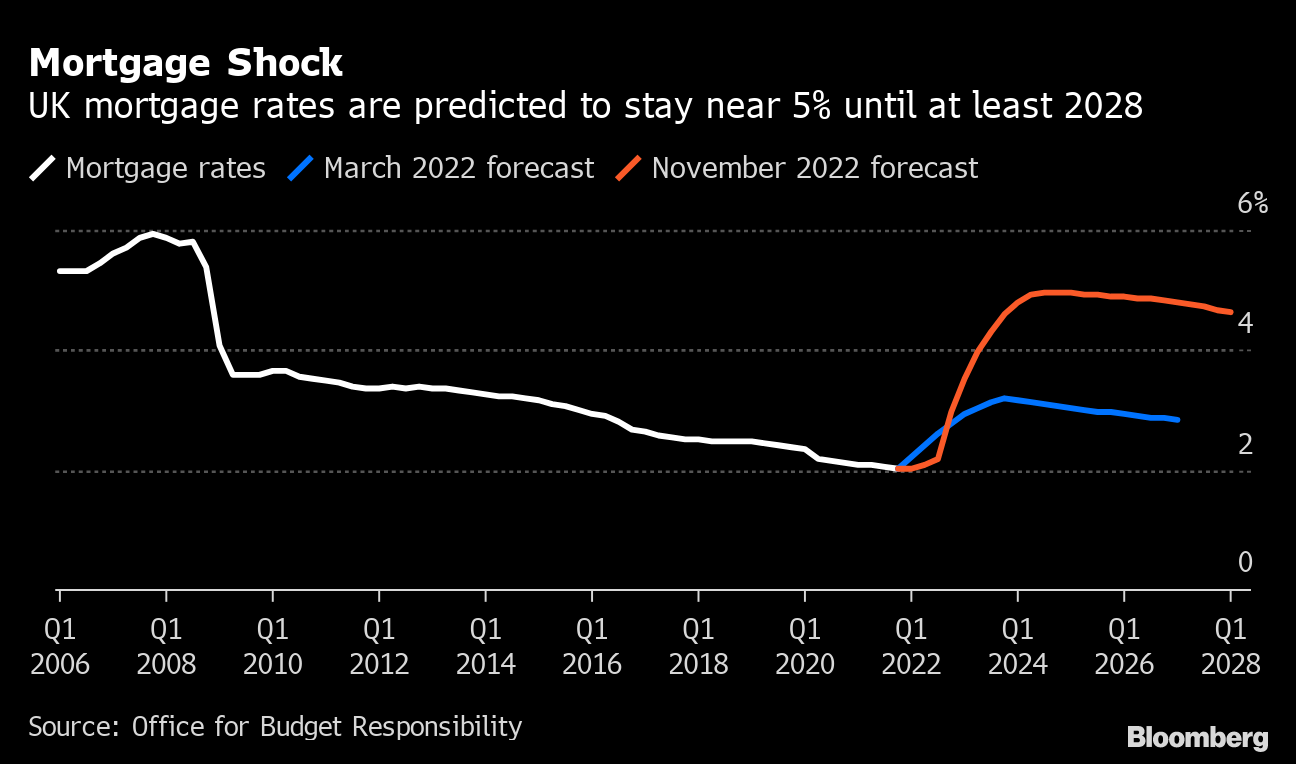
The ongoing geopolitical tensions, particularly the Russia-Ukraine conflict, have created a volatile environment for global markets and have contributed to inflationary pressures. The war has disrupted supply chains, driven up energy prices, and introduced uncertainty into the global economic outlook. The potential for further escalation of geopolitical tensions, particularly in regions like the Indo-Pacific, could further complicate the economic landscape and influence central bank decisions regarding interest rates.
Technological Advancements: A Double-Edged Sword
Technological advancements, while often touted as a driver of economic growth, can also contribute to inflationary pressures. The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and other transformative technologies can lead to increased productivity, but it can also disrupt labor markets and create new challenges for policymakers. The impact of technological advancements on interest rates in 2025 will depend on the extent to which these technologies contribute to inflation or deflationary pressures.
Emerging Market Dynamics: A Source of Volatility
Emerging markets face unique challenges in navigating the current global economic environment. Rising interest rates in developed economies can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets, putting pressure on their currencies and potentially triggering financial instability. The ability of emerging market economies to manage their debt burdens and maintain macroeconomic stability will be crucial in determining their resilience to global interest rate trends in 2025.
Scenario Analysis: Potential Interest Rate Trajectories in 2025
To understand the potential impact of these factors on interest rates in 2025, it is useful to consider different scenarios:
Scenario 1: A Soft Landing
This scenario assumes that central banks successfully manage to tame inflation without triggering a recession. Inflation gradually moderates, economic growth remains relatively stable, and geopolitical tensions ease. In this scenario, interest rates are likely to stabilize at a higher level than pre-pandemic levels, but they will not continue to rise significantly.
Scenario 2: A Stagflationary Environment
This scenario envisions a persistent period of high inflation and sluggish economic growth. Central banks are unable to control inflation effectively, leading to continued interest rate hikes. This scenario could result in a sharp rise in interest rates, potentially leading to a recession and a prolonged period of economic stagnation.
Scenario 3: A Global Recession
This scenario assumes that the global economy enters a recession, triggered by a combination of factors such as high inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical tensions. Central banks may be forced to cut interest rates in an attempt to stimulate economic growth, but the effectiveness of such measures could be limited in a recessionary environment.
Implications for Businesses, Investors, and Individuals
The potential trends in interest rates in 2025 will have significant implications for businesses, investors, and individuals:
Businesses:
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher interest rates will increase the cost of borrowing for businesses, potentially impacting their investment decisions and profitability.
- Reduced consumer demand: Rising interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs for consumers, potentially reducing their spending and impacting business revenue.
- Investment opportunities: Businesses may need to adjust their investment strategies to account for the higher cost of capital and the potential impact of interest rate changes on their operations.
Investors:
- Bond market volatility: Interest rate changes can significantly impact the value of bonds, creating volatility in the bond market.
- Equity market performance: Higher interest rates can impact corporate profitability and potentially lead to lower stock valuations.
- Portfolio diversification: Investors may need to adjust their portfolio allocations to account for the potential impact of interest rate changes on different asset classes.
Individuals:
- Higher borrowing costs: Rising interest rates will make it more expensive to borrow money for mortgages, auto loans, and other personal loans.
- Reduced savings returns: Higher interest rates can lead to lower returns on savings accounts and other fixed-income investments.
- Increased cost of living: Higher interest rates can contribute to higher inflation, leading to increased costs for goods and services.
Conclusion: Navigating the Uncertainty
The path of interest rates in 2025 remains uncertain, influenced by a complex interplay of factors. While the specific trajectory of interest rates is difficult to predict with certainty, understanding the potential scenarios and their implications is essential for businesses, investors, and individuals to navigate the economic landscape effectively. By staying informed, being adaptable, and making informed decisions, stakeholders can mitigate the potential risks and capitalize on the opportunities presented by the evolving interest rate environment.
Looking Ahead:
- Continued Monitoring: It is essential to closely monitor inflation data, central bank announcements, and geopolitical developments to gain insights into the evolving interest rate landscape.
- Scenario Planning: Businesses, investors, and individuals should develop scenario plans to assess the potential impact of different interest rate scenarios on their operations, investment decisions, and financial well-being.
- Risk Management: Implement robust risk management strategies to mitigate the potential negative impacts of interest rate changes.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adjust strategies and plans as needed to respond to changing economic conditions and interest rate trends.
In conclusion, the journey towards 2025 is fraught with uncertainty, but by understanding the key factors influencing interest rates and by adopting a proactive and adaptable approach, stakeholders can navigate the uncharted waters and position themselves for success.



![[Transformational] Navigating the Waters of US Interest Rates: Current](https://all-jisik.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/DALL%C2%B7E-2023-11-20-17.38.09-A-detailed-illustration-of-a-graph-showing-US-interest-rates-over-time.-The-graph-starts-from-2023-and-extends-into-2024-depicting-a-gradual-decline--768x768.png)
