Navigating The Future: Healthcare Trends Shaping 2025
Navigating the Future: Healthcare Trends Shaping 2025
The healthcare landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving patient expectations, and a growing global population. As we approach 2025, several key trends are poised to reshape the way we access, experience, and deliver healthcare. This article will explore these trends, examining their potential impact on patients, providers, and the overall healthcare ecosystem.
1. The Rise of Personalized and Precision Medicine:
Personalized medicine, tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup and lifestyle, is a transformative force in healthcare. This trend is fueled by the rapid advancements in genomics, bioinformatics, and artificial intelligence (AI).
- Genomics and Personalized Treatments: Genetic testing is becoming increasingly affordable and accessible, allowing doctors to identify genetic predispositions to diseases and tailor treatment plans accordingly. This personalized approach is revolutionizing cancer treatment, cardiovascular care, and rare disease diagnosis.
- Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapies: Precision medicine focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying diseases, leading to the development of targeted therapies that effectively address specific disease pathways. This approach is proving highly effective in treating certain cancers, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
- AI-powered Diagnosis and Treatment: AI algorithms are being used to analyze vast amounts of patient data, including genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, to predict disease risk, identify potential treatment options, and even personalize drug dosages.
Impact: This trend will lead to more effective and efficient healthcare, reducing unnecessary treatments and improving patient outcomes. However, ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and equitable access to personalized medicine will need careful attention.
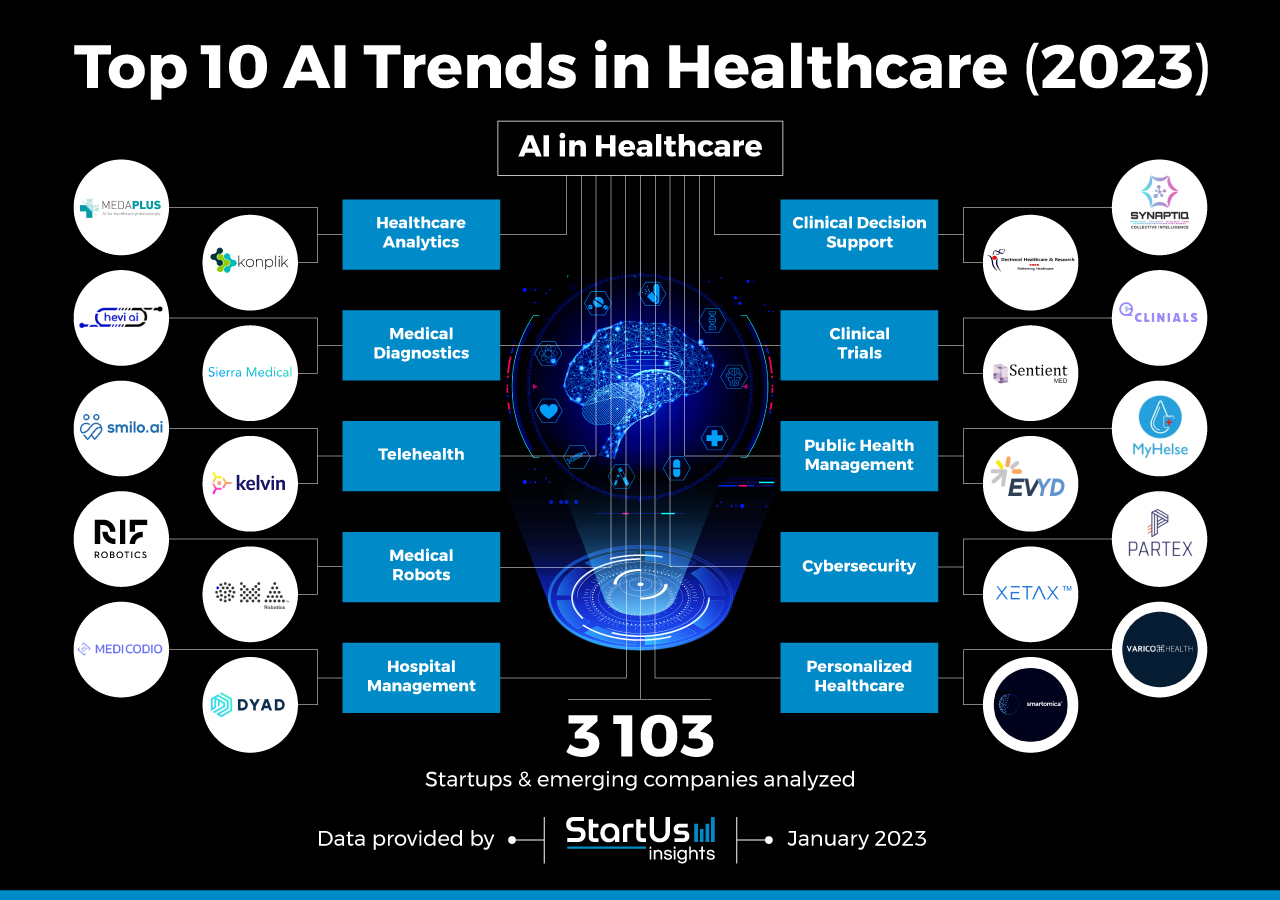
2. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML are rapidly transforming healthcare, automating tasks, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, and improving patient care.
- AI-powered Diagnosis and Prognosis: AI algorithms can analyze medical images, lab results, and patient data to detect subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human eyes. This can lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of diseases like cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s.
- Robotic Surgery and Minimally Invasive Procedures: AI-powered robotic systems are revolutionizing surgical procedures, enabling greater precision, faster recovery times, and reduced complications.
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots are providing patients with 24/7 access to healthcare information, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI is accelerating drug discovery and development by analyzing vast datasets to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety.
Impact: AI and ML will significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex patient care. However, concerns about potential job displacement and the need for ethical guidelines for AI use in healthcare must be addressed.
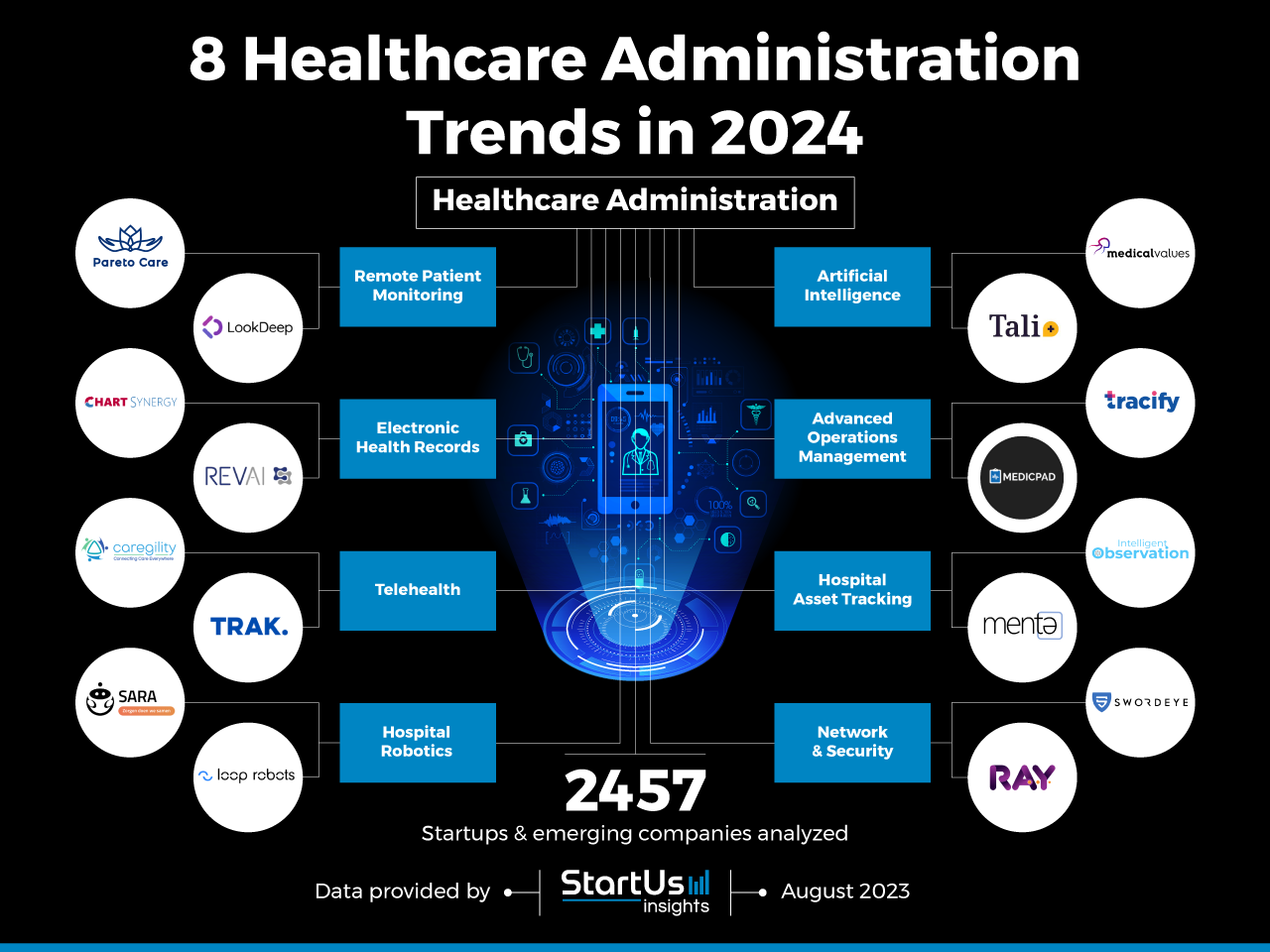
3. The Expansion of Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring:
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth, and this trend is expected to continue in the years to come.
- Virtual Consultations and Remote Monitoring: Telehealth allows patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely via video conferencing, phone calls, or mobile apps. This provides convenient access to healthcare, especially for those in rural or underserved areas.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Devices: Wearable devices and home-based monitoring systems allow patients to track their vital signs and health data remotely, enabling early detection of health issues and proactive management of chronic conditions.
- Remote Rehabilitation and Therapy: Telehealth platforms are facilitating remote rehabilitation and therapy sessions, providing patients with access to specialized care from the comfort of their own homes.
Impact: Telehealth will increase access to healthcare services, improve patient engagement, and reduce healthcare costs. However, ensuring secure data transmission and maintaining patient privacy will be crucial.
4. The Rise of Consumer-Centric Healthcare:
Patients are becoming increasingly empowered and demanding more control over their healthcare decisions.
- Patient Portals and Data Access: Patient portals allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, and communicate with their providers online. This empowers patients to take an active role in their healthcare.
- Direct-to-Consumer Healthcare Services: Direct-to-consumer healthcare services, such as telehealth platforms and home-based diagnostics, are offering patients convenient and affordable alternatives to traditional healthcare models.
- Personalized Health Plans and Wellness Programs: Healthcare providers are developing personalized health plans and wellness programs that cater to individual patient needs and preferences.
Impact: This trend is driving innovation in healthcare delivery, but it also poses challenges for healthcare providers who need to adapt to patient expectations and meet the growing demand for personalized care.
5. The Importance of Data Security and Privacy:
As healthcare becomes increasingly digital, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount.
- Data Encryption and Secure Storage: Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive patient data from unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe are crucial for safeguarding patient privacy and ensuring ethical data handling practices.
- Data Interoperability and Information Sharing: Enabling seamless data sharing between healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy is essential for improving patient care and reducing medical errors.
Impact: Investing in robust data security infrastructure and adhering to privacy regulations are essential for building trust and confidence in digital healthcare.
6. The Growing Importance of Mental Health and Wellness:
Mental health is increasingly recognized as an integral part of overall health and well-being.
- Integrated Mental Health Care: Mental health services are being integrated into primary care settings, making it easier for patients to access mental health support.
- Digital Mental Health Tools: Apps and online platforms are providing patients with access to mental health resources, self-help tools, and online therapy sessions.
- Focus on Prevention and Early Intervention: Efforts are being made to address mental health issues through prevention programs and early intervention strategies.
Impact: This trend will improve access to mental health care and reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues. However, addressing the shortage of mental health professionals and ensuring equitable access to mental health services will be crucial.
7. The Focus on Value-Based Care:
Value-based care models aim to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs by rewarding providers for delivering high-quality care.
- Population Health Management: Healthcare providers are taking a proactive approach to managing the health of entire populations, focusing on preventive care and early intervention.
- Pay-for-Performance Models: Providers are incentivized to deliver high-quality care by being rewarded based on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services provided.
- Data Analytics and Performance Measurement: Data analytics is used to track patient outcomes, identify areas for improvement, and measure the effectiveness of healthcare interventions.
Impact: Value-based care models are expected to drive innovation in healthcare delivery, leading to more efficient and effective care. However, implementing these models effectively requires robust data infrastructure, strong provider collaboration, and clear performance metrics.
8. The Role of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare:
Blockchain technology, known for its security and transparency, is finding applications in healthcare.
- Secure Data Storage and Sharing: Blockchain can provide a secure and tamper-proof platform for storing and sharing patient data, enhancing data security and privacy.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track the movement of medical supplies and pharmaceuticals, ensuring their authenticity and safety.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Blockchain can facilitate the secure sharing of EHRs between healthcare providers, improving interoperability and reducing the risk of medical errors.
Impact: Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize healthcare data management and create a more transparent and secure healthcare ecosystem. However, widespread adoption requires overcoming technical challenges and addressing regulatory concerns.
9. The Growing Importance of Health Equity:
Addressing health disparities and promoting health equity is becoming increasingly crucial.
- Social Determinants of Health: Healthcare providers are recognizing the impact of social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and access to healthy food, on patient outcomes.
- Community Health Initiatives: Efforts are being made to address health disparities through community-based health initiatives and culturally competent care.
- Data-driven Interventions: Data analytics is being used to identify and address health disparities, targeting interventions to communities with the greatest need.
Impact: Achieving health equity requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses social determinants of health, promotes culturally competent care, and ensures equitable access to healthcare services.
10. The Evolution of Healthcare Workforce:
The healthcare workforce is evolving to meet the changing needs of the healthcare system.
- Shortage of Healthcare Professionals: The growing demand for healthcare services is leading to a shortage of physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals.
- Rise of Non-Physician Healthcare Providers: The role of non-physician healthcare providers, such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants, is expanding to address the growing demand for care.
- Telehealth and Remote Workforce: The adoption of telehealth is creating opportunities for healthcare professionals to work remotely, expanding access to care and improving work-life balance.
Impact: Addressing the healthcare workforce shortage and adapting to the changing needs of the workforce will be crucial for ensuring access to high-quality healthcare in the future.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While these trends hold immense promise for improving healthcare, they also present challenges:
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI, genomics, and other emerging technologies raises ethical concerns about data privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access to healthcare.
- Regulatory Landscape: The rapid pace of technological advancements requires a flexible and adaptable regulatory framework to ensure patient safety and ethical use of new technologies.
- Cost and Access: The cost of implementing new technologies and expanding access to healthcare services remains a significant challenge, particularly in developing countries.
Conclusion:
The future of healthcare is bright with opportunities to improve patient outcomes, enhance access to care, and create a more equitable healthcare system. By embracing these trends, leveraging technological advancements, and addressing the challenges head-on, we can navigate the future of healthcare and build a healthier world for all.
The journey towards a more personalized, data-driven, and equitable healthcare system is just beginning. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing patient well-being, we can shape a future where healthcare is truly accessible, effective, and patient-centered.