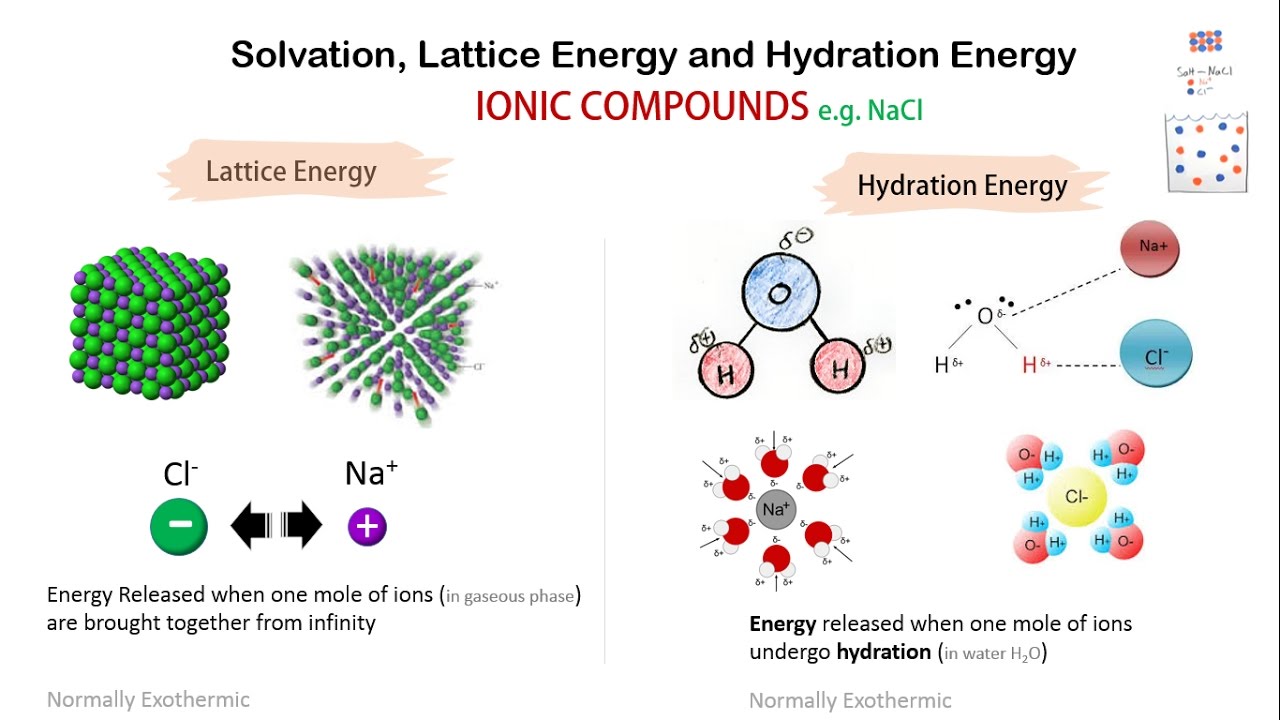
Lattice Energy Trends: 2025 And Beyond
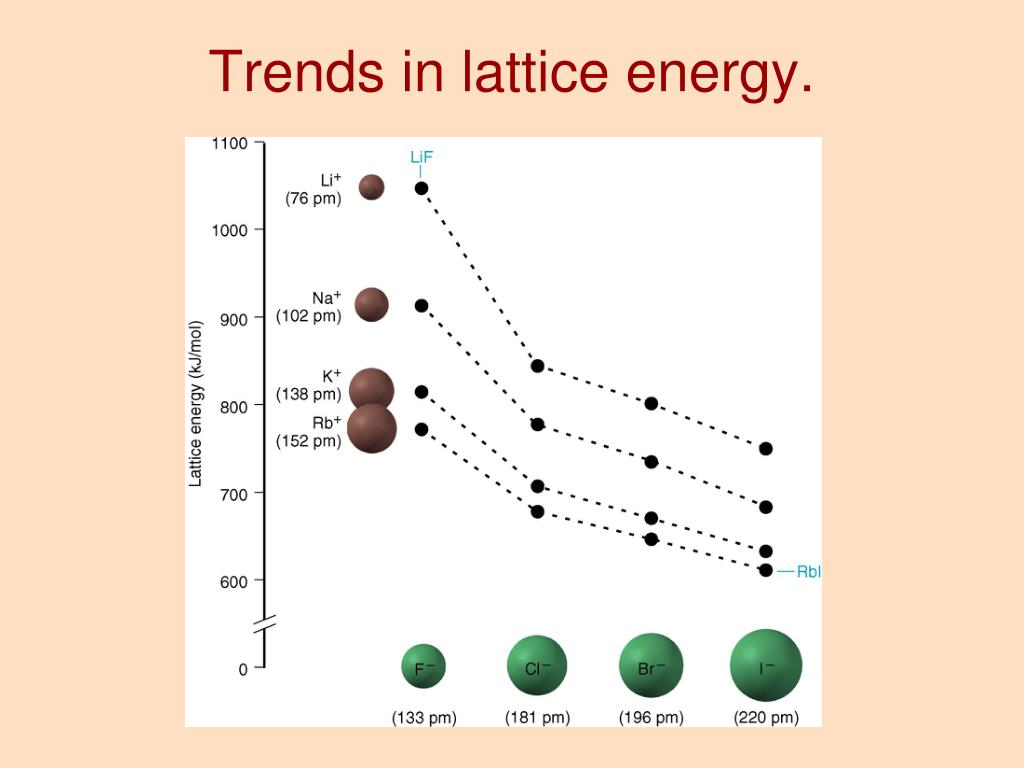
Lattice Energy Trends: 2025 and Beyond
Lattice energy, the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of one mole of a crystalline ionic compound from its gaseous ions, serves as a fundamental cornerstone in understanding the stability and properties of ionic materials. As we approach 2025, the field of lattice energy research is experiencing a dynamic evolution, driven by advancements in theoretical modeling, experimental techniques, and the burgeoning demand for innovative materials across diverse technological domains. This article delves into the prominent trends shaping the landscape of lattice energy research in 2025 and beyond, highlighting the interplay between fundamental understanding and practical applications.
1. The Rise of High-Throughput Computational Screening
The exponential growth of computational power has revolutionized the way we approach lattice energy calculations. High-throughput screening (HTS) methods, coupled with sophisticated quantum mechanical models, enable the efficient evaluation of lattice energies for vast libraries of potential ionic compounds. This approach allows researchers to:
- Identify promising candidates: HTS can rapidly identify materials with desirable lattice energies, guiding the synthesis of novel compounds with tailored properties. For instance, in the field of battery materials, researchers can screen for compounds exhibiting high lattice energies, ensuring robust crystal structures and enhanced cycling stability.
- Optimize existing materials: HTS can be used to fine-tune the composition and structure of existing materials, aiming to maximize their lattice energies and improve their performance in specific applications. This approach is particularly relevant for developing advanced ceramics, catalysts, and energy storage materials.
- Uncover novel trends: By systematically varying the ionic radii, charges, and electronic configurations of ions, HTS enables the identification of complex relationships between ionic composition and lattice energy. This data-driven approach can lead to the discovery of new trends and predictive models for lattice energy behavior.
2. Unveiling the Role of Interplay Between Ions
While traditional models often focus on the electrostatic interactions between point charges, the intricacies of lattice energy are increasingly being attributed to the interplay between ions beyond simple Coulombic forces. This nuanced understanding is driven by:
- Polarizability effects: The ability of ions to distort their electron clouds under the influence of neighboring ions plays a crucial role in determining lattice energy. Advanced computational methods are now incorporating polarizability effects, providing a more accurate description of the interactions between ions.
- Covalency contributions: In many ionic compounds, a degree of covalent bonding exists, contributing to the overall lattice energy. Quantum chemical calculations, such as Density Functional Theory (DFT), are increasingly employed to quantify these covalent contributions, offering a more comprehensive picture of the bonding landscape.
- Beyond the pairwise approximation: The traditional pairwise approximation, which considers only interactions between pairs of ions, is being challenged by the emergence of many-body interactions. These interactions, arising from the collective behavior of multiple ions, are crucial for understanding complex phenomena like cooperative distortions and phase transitions in ionic materials.
3. Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Experiment
The integration of theoretical modeling with experimental techniques is crucial for achieving a comprehensive understanding of lattice energy. This synergy enables researchers to:
- Validate theoretical predictions: Experimental measurements of lattice energies, obtained through techniques like calorimetry and diffraction, provide a crucial benchmark for validating theoretical calculations. This validation process ensures the accuracy and reliability of theoretical models.
- Guide theoretical development: Discrepancies between theoretical predictions and experimental observations can highlight limitations in existing models, prompting the development of more sophisticated theoretical frameworks. This iterative process leads to continuous refinement of theoretical tools.
- Uncover new insights: Combining theoretical and experimental approaches allows researchers to investigate phenomena that are difficult to study solely through theory or experiment. For instance, the combination of X-ray diffraction and DFT calculations can reveal the subtle changes in ionic positions and electronic structure that occur during phase transitions.
4. Pushing the Boundaries of Experimental Techniques
Experimental techniques for measuring lattice energies are undergoing significant advancements, enabling more precise and versatile measurements:
- High-pressure calorimetry: The development of high-pressure calorimeters allows researchers to study the effect of pressure on lattice energy, providing valuable insights into the stability and compressibility of ionic materials. This approach is particularly relevant for understanding the behavior of materials under extreme conditions, such as those encountered in planetary interiors.
- Time-resolved spectroscopy: Time-resolved spectroscopy techniques enable the study of dynamic processes, such as the formation and dissociation of ionic bonds, providing insights into the kinetics and mechanisms underlying lattice energy changes. These techniques are crucial for understanding the behavior of ionic materials under non-equilibrium conditions.
- In situ characterization: In situ characterization techniques, such as X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy, allow researchers to study the structural and electronic properties of ionic materials in real-time during synthesis, processing, or application. This approach provides a direct link between the microscopic structure and macroscopic properties of ionic materials, offering valuable insights into the relationship between lattice energy and performance.
5. Harnessing Lattice Energy for Innovative Applications
The understanding of lattice energy is crucial for developing materials with tailored properties for a wide range of applications:
- Energy storage and conversion: Materials with high lattice energies are desirable for battery electrodes, ensuring robust structures and enhanced cycling stability. Understanding the interplay between lattice energy and ionic conductivity is critical for developing efficient solid-state electrolytes.
- Catalysis: Lattice energy plays a crucial role in determining the reactivity and selectivity of catalysts. By tuning the lattice energy of catalytic materials, researchers can optimize their performance for specific chemical reactions.
- Ceramics and refractories: High lattice energies contribute to the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance of ceramics and refractories. This understanding is essential for developing materials for high-temperature applications, such as in aerospace and energy production.
- Biomaterials: Lattice energy plays a role in the biocompatibility and bioactivity of biomaterials. Understanding the relationship between lattice energy and biocompatibility can lead to the development of new materials for bone implants, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
6. Emerging Trends in Lattice Energy Research
As we move beyond 2025, the field of lattice energy research is poised to embrace exciting new frontiers:
- Multiscale modeling: Bridging the gap between atomistic simulations and macroscopic properties will require the development of multiscale modeling techniques. These techniques will integrate quantum mechanical calculations with coarse-grained models, enabling the prediction of material behavior across multiple length scales.
- Machine learning: Machine learning algorithms are increasingly being employed to analyze vast datasets of lattice energy calculations, identifying complex relationships and predicting the properties of new materials. This data-driven approach can accelerate the discovery and development of novel materials.
- Experimental-theoretical feedback loop: The continuous interplay between theoretical predictions and experimental observations will lead to a virtuous cycle of refinement and innovation. This feedback loop will drive the development of more accurate theoretical models and enable the design of materials with unprecedented properties.
- Focus on sustainability: The development of environmentally friendly materials with high lattice energies is becoming increasingly important. Researchers are exploring the use of abundant and sustainable elements, such as magnesium and aluminum, to create high-performance materials with reduced environmental impact.
Conclusion:
The field of lattice energy research is undergoing a period of rapid transformation, driven by advancements in computational modeling, experimental techniques, and the increasing demand for innovative materials. By understanding the intricate interplay between ions and the role of lattice energy in determining material properties, researchers are poised to develop materials with unprecedented performance for a wide range of applications. As we move beyond 2025, the ongoing integration of theory and experiment, combined with the emergence of new tools and techniques, promises a future where lattice energy research will play an even more central role in shaping the materials of tomorrow.