ETF Trends 2025: Navigating A World Of Innovation And Disruption
ETF Trends 2025: Navigating a World of Innovation and Disruption
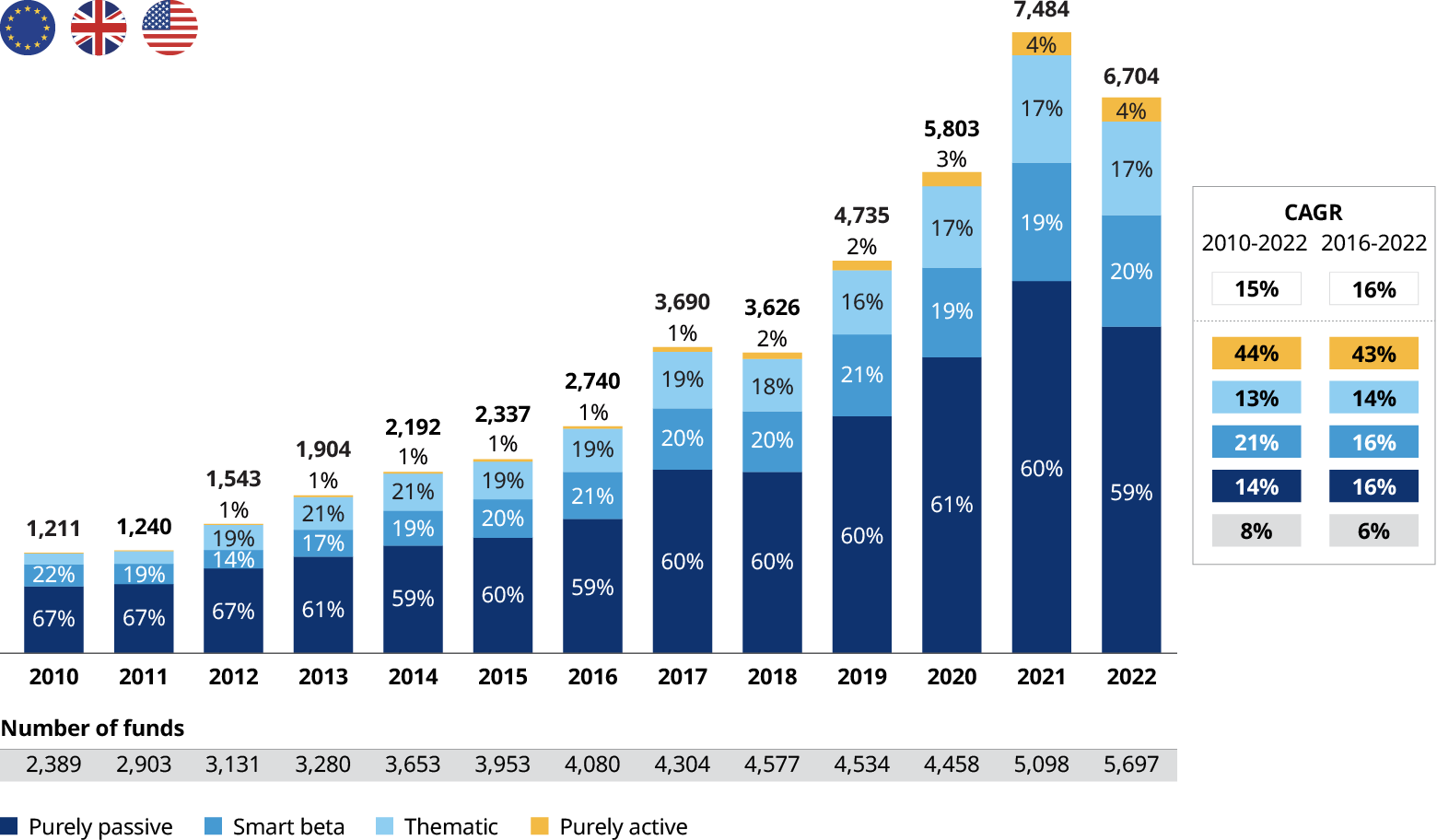
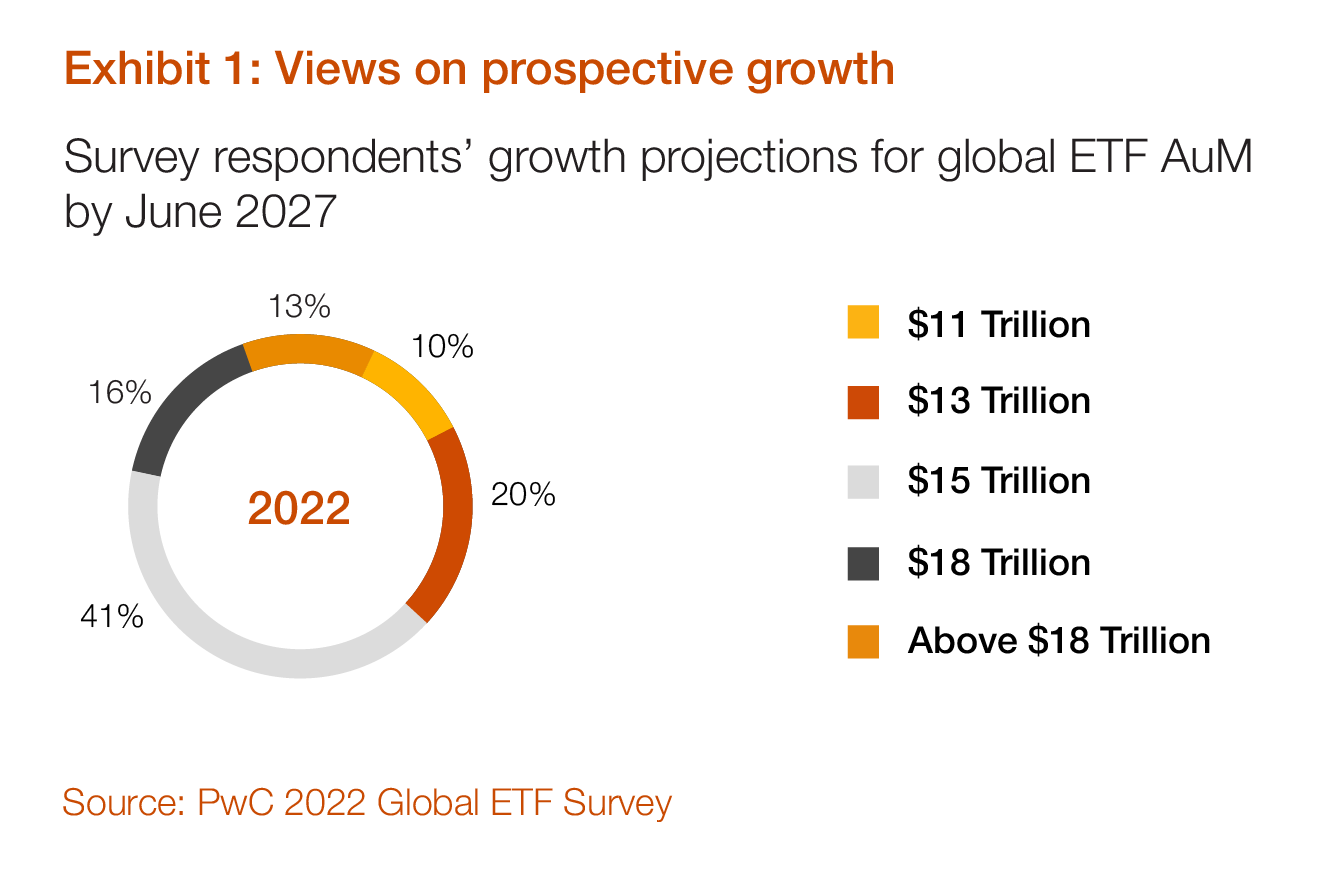
The ETF landscape is undergoing a dramatic evolution, driven by technological advancements, evolving investor preferences, and a rapidly changing global economic landscape. As we look ahead to 2025, several key trends are poised to shape the future of exchange-traded funds, offering both opportunities and challenges for investors.
1. The Rise of Thematic ETFs:
Thematic ETFs, which track a specific investment theme like artificial intelligence, clean energy, or cybersecurity, have exploded in popularity in recent years. This trend is expected to continue, driven by several factors:
- Growing Investor Interest in Specific Sectors: Investors increasingly seek to align their portfolios with their values and beliefs, investing in areas they believe are poised for growth. Thematic ETFs provide a convenient way to access these sectors.
- Technological Advancements: The rise of artificial intelligence and big data analysis is allowing ETF providers to create more sophisticated thematic strategies. This leads to more targeted and potentially higher-performing products.
- Increased Complexity of Traditional Asset Classes: The traditional asset classes, like stocks and bonds, are becoming increasingly complex, making it challenging for investors to navigate. Thematic ETFs offer a simpler and more focused approach to investing.
2. The Democratization of Alternative Investments:
Alternative investments, traditionally accessible only to institutional investors, are becoming more accessible through ETFs. This trend is driven by:
- Increased Demand for Diversification: Investors seek to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional assets to enhance returns and mitigate risk. Alternative investments, like private equity, real estate, and commodities, offer unique diversification benefits.
- Technological Innovations: Blockchain technology and other innovations are making it easier to track and trade alternative investments through ETFs. This lowers the barriers to entry for individual investors.
- Growing Regulatory Clarity: Increased regulatory clarity and standardization are making it easier for ETF providers to offer alternative investment products.
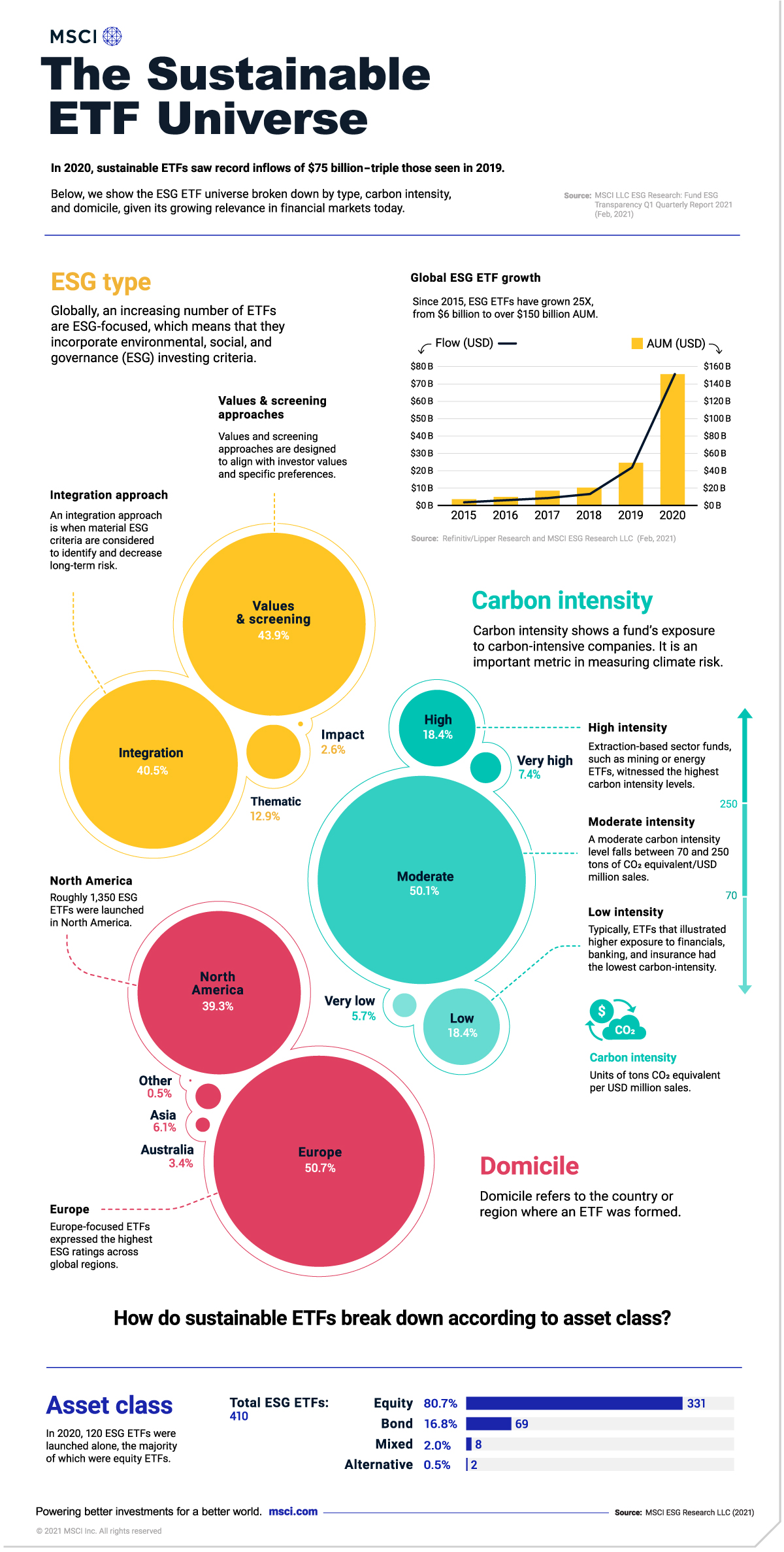
3. The Expansion of ESG Investing:
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing is gaining momentum, with investors increasingly prioritizing sustainability and ethical considerations in their investment decisions. This trend is reflected in the growing number of ESG-focused ETFs:
- Increasing Investor Demand: A growing number of investors are seeking to align their investments with their values, investing in companies that prioritize sustainability and social responsibility.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments and regulators are increasingly focusing on sustainability and ESG factors, creating a more favorable environment for ESG investing.
- Increased Transparency and Data Availability: The availability of better data and reporting standards makes it easier for investors to assess the ESG performance of companies and ETFs.
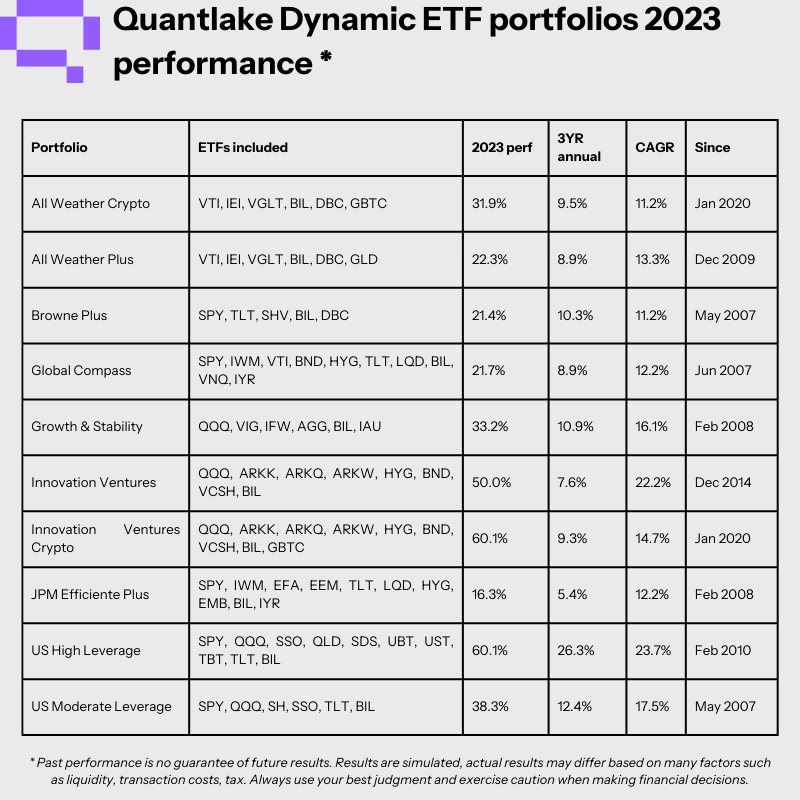
4. The Emergence of Active ETFs:
Active ETFs, which use strategies to outperform the market, are gaining traction as investors seek to enhance returns in a low-interest rate environment. This trend is driven by:
- The Search for Alpha: Investors are increasingly seeking to generate alpha (outperformance) in a market where traditional passive strategies are struggling to deliver significant returns.
- Technological Advancements: The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in active ETFs is making it easier to develop and manage complex strategies.
- Growing Competition: The rise of active ETFs is increasing competition in the ETF market, leading to more innovative and potentially higher-performing products.
5. The Rise of Fractional Investing:
Fractional investing, which allows investors to buy small portions of shares in high-priced assets, is becoming increasingly popular, particularly among younger investors. This trend is driven by:
- Accessibility and Affordability: Fractional investing makes it easier for investors with limited capital to access high-priced assets like stocks and ETFs.
- Increased Financial Literacy: The rise of online investing platforms and educational resources is making it easier for investors to learn about fractional investing.
- Democratization of Investing: Fractional investing empowers more people to participate in the market, regardless of their income level.
6. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI is transforming the ETF industry, from portfolio construction and risk management to investor engagement and product development:
- Automated Portfolio Management: AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to create and manage portfolios more efficiently and effectively.
- Enhanced Risk Management: AI can identify and mitigate risks more effectively, helping to protect investors from market volatility.
- Personalized Investment Advice: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized investment advice and support to investors.
- Improved Product Development: AI can help ETF providers to develop new and innovative products that meet the evolving needs of investors.
7. The Growing Importance of Data and Analytics:
Data and analytics are becoming increasingly crucial for ETF providers and investors alike:
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: ETF providers are using data analytics to identify investment opportunities, manage risk, and improve portfolio performance.
- Enhanced Investor Transparency: Data and analytics are making it easier for investors to understand the performance and risk characteristics of ETFs.
- Personalized Investment Experiences: Data analytics can be used to create personalized investment experiences, tailored to the specific needs and preferences of investors.
8. The Evolution of ETF Distribution:
The distribution of ETFs is evolving as new channels emerge and investor preferences shift:
- Direct-to-Consumer Platforms: The rise of online investing platforms is making it easier for investors to buy and sell ETFs directly, without the need for a traditional brokerage account.
- Robo-Advisors: Robo-advisors are using algorithms to create and manage ETF portfolios based on investor goals and risk tolerance.
- Mobile Investing Apps: Mobile investing apps are making it easier for investors to access and manage their ETF investments on the go.
9. The Growing Role of Fintech:
Fintech companies are disrupting the ETF industry, offering innovative solutions for portfolio management, trading, and investor education:
- Automated Trading Platforms: Fintech companies are developing automated trading platforms that use AI to execute trades more efficiently and effectively.
- Personalized Investment Tools: Fintech companies are offering personalized investment tools that help investors to identify and manage their investments more effectively.
- Enhanced Investor Education: Fintech companies are providing educational resources and tools that make it easier for investors to learn about ETFs and other investment products.
10. The Impact of Regulatory Changes:
Regulatory changes are shaping the ETF landscape, impacting product development, distribution, and investor protection:
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing the ETF industry, particularly with regard to transparency, risk management, and investor protection.
- New Regulations and Guidelines: Regulators are introducing new regulations and guidelines to address emerging risks and challenges in the ETF market.
- Increased Compliance Costs: The increased regulatory scrutiny is leading to higher compliance costs for ETF providers.
Challenges and Opportunities for Investors:
The trends outlined above present both challenges and opportunities for investors:
Challenges:
- Increased Complexity: The ETF market is becoming increasingly complex, with a wider range of products and strategies to choose from.
- Information Overload: The vast amount of information available about ETFs can be overwhelming for investors.
- Market Volatility: The ETF market is subject to market volatility, which can impact the performance of investments.
Opportunities:
- Greater Access to Investment Opportunities: ETFs offer investors access to a wide range of asset classes and investment strategies.
- Improved Diversification: ETFs can help investors to diversify their portfolios and reduce risk.
- Cost-Effectiveness: ETFs are generally more cost-effective than mutual funds, with lower expense ratios.
Navigating the Future of ETFs:
To navigate the evolving ETF landscape, investors should:
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest trends and developments in the ETF market.
- Do Your Research: Thoroughly research ETFs before investing, considering factors such as expense ratios, performance history, and underlying assets.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with a financial advisor to develop a personalized investment strategy that aligns with your goals and risk tolerance.
- Embrace Technology: Leverage technology to access information, manage investments, and stay informed about market trends.
Conclusion:
The ETF industry is on the cusp of a transformative era, driven by technological advancements, changing investor preferences, and a rapidly evolving global economic landscape. As we look ahead to 2025, investors have a unique opportunity to harness the power of ETFs to achieve their financial goals and navigate the complexities of a dynamic investment world. By staying informed, conducting thorough research, and embracing the latest technological innovations, investors can position themselves for success in the evolving ETF landscape.