Data In 2025: A Landscape Of Exponential Growth And Ethical Dilemmas
Data in 2025: A Landscape of Exponential Growth and Ethical Dilemmas
The data landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by the exponential growth of data generation, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), and the increasing adoption of cloud computing. As we stand on the cusp of 2025, the future of data holds both immense potential and complex challenges. This article explores key trends shaping the data landscape in the coming years, examining the opportunities and ethical considerations that will define this dynamic field.
1. The Data Explosion Continues: A Tsunami of Information
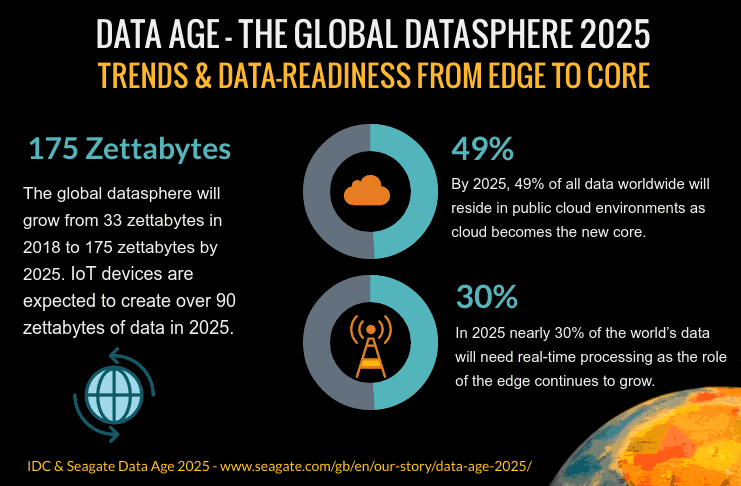
The volume of data generated worldwide is growing at an unprecedented rate. By 2025, we are projected to generate over 175 zettabytes of data annually, a figure that dwarfs even the most ambitious predictions of the past. This data tsunami will be fueled by the proliferation of connected devices, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), and the increasing adoption of data-intensive applications in various sectors.
a) The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT): A Network of Data Points
The IoT, with its interconnected devices and sensors, will be a major contributor to the data explosion. From smart homes and cities to industrial automation and healthcare, the IoT will generate massive amounts of real-time data, providing valuable insights into various aspects of our lives and industries.
b) Data-Driven Applications: Transforming Industries
Industries across the spectrum are embracing data-driven applications. From personalized medicine and smart agriculture to financial modeling and predictive maintenance, data is becoming the cornerstone of innovation and efficiency. This shift towards data-driven decision-making will fuel further data generation and demand for advanced data analytics capabilities.
2. The Power of AI: Unleashing Data’s Potential
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a transformative role in harnessing the power of data. Advanced AI algorithms are capable of processing and analyzing vast datasets, uncovering hidden patterns and generating insights that would be impossible for humans to achieve.
a) Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Unveiling Patterns and Insights
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms are at the forefront of AI-powered data analysis. These algorithms can learn from data, adapt to changing conditions, and make predictions with increasing accuracy. From fraud detection and risk assessment to personalized recommendations and natural language processing, ML and DL are revolutionizing various industries.
b) AI-Driven Automation: Streamlining Processes and Boosting Efficiency
AI is enabling automation in various tasks, from customer service and content creation to data entry and financial analysis. This automation not only increases efficiency but also frees up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors.
3. Cloud Computing: The Backbone of Data Management
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and scalability needed to manage the ever-growing volume of data. Cloud platforms offer flexible storage solutions, powerful computing resources, and advanced data analytics tools, making it easier for organizations of all sizes to leverage data effectively.
a) The Rise of Hybrid Cloud Solutions: Combining Flexibility and Security
Hybrid cloud solutions, combining public and private cloud environments, are gaining popularity, offering greater flexibility and security. This approach allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both cloud models, optimizing data management and security based on their specific needs.
b) Edge Computing: Bringing Data Processing Closer to the Source
Edge computing is emerging as a vital component of data management, bringing data processing closer to the source of data generation. This approach reduces latency, improves real-time insights, and enhances the efficiency of data-driven applications.
4. Data Governance and Security: Addressing Ethical Challenges
The increasing volume and sensitivity of data raise significant ethical and security concerns. Data governance and security measures are crucial to ensure responsible data usage, protect privacy, and maintain trust in data-driven systems.
a) Data Privacy and Security Regulations: Shaping the Data Landscape
Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are shaping the data landscape, emphasizing data protection and user privacy. Organizations must comply with these regulations to avoid legal repercussions and maintain public trust.
b) Data Ethics and Responsible AI: Guiding Principles for Data Usage
Data ethics and responsible AI are becoming increasingly important as AI systems become more prevalent. Guidelines and frameworks are being developed to ensure that AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable, preventing bias and promoting ethical data usage.
5. Data Democratization: Making Data Accessible to All
Data democratization aims to make data accessible to everyone, empowering individuals and organizations to leverage data for innovation and decision-making. This trend is driven by the increasing availability of data visualization tools, open data initiatives, and the growing adoption of citizen data science.
a) Data Visualization Tools: Making Data Understandable and Engaging
Data visualization tools are making data more accessible and understandable. These tools transform complex data into interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards, enabling users to gain insights and communicate findings effectively.
b) Open Data Initiatives: Promoting Transparency and Collaboration
Open data initiatives encourage the sharing and reuse of public data, promoting transparency and collaboration. This approach fosters innovation, empowers citizen engagement, and drives economic growth.
6. Emerging Trends: Shaping the Future of Data
The data landscape is constantly evolving, with emerging trends pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. These trends are shaping the future of data, offering new opportunities and challenges.
a) The Rise of Quantum Computing: Unlocking New Possibilities for Data Analysis
Quantum computing, with its ability to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, holds immense potential for data analysis. Quantum algorithms can accelerate machine learning, optimize data storage, and unlock new possibilities in data-driven applications.
b) Synthetic Data Generation: Addressing Privacy Concerns and Enabling Innovation
Synthetic data generation techniques create artificial datasets that mimic real-world data while protecting privacy. This approach enables data analysis and model development without compromising sensitive information, facilitating innovation and research.
c) The Metaverse and Web 3.0: Redefining Data Interaction and Ownership
The metaverse and Web 3.0 are transforming data interaction and ownership. These emerging technologies enable decentralized data storage, user-controlled data sharing, and immersive data experiences, opening up new possibilities for data utilization and collaboration.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Data Landscape
The future of data is not without its challenges. As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, organizations face challenges in managing, analyzing, and securing this data effectively. However, these challenges also present significant opportunities for innovation, growth, and societal progress.
a) Bridging the Data Skills Gap: Cultivating a Data-Literate Workforce
The growing demand for data professionals is creating a significant skills gap. Organizations need to invest in training and education programs to develop a data-literate workforce capable of managing, analyzing, and interpreting data effectively.
b) Fostering Data Literacy: Empowering Individuals and Organizations
Data literacy is crucial for individuals and organizations to navigate the data-driven world. Educational initiatives, accessible data visualization tools, and clear communication strategies can empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions based on data.
c) Ethical Considerations: Ensuring Responsible Data Usage
As AI and data-driven systems become more prevalent, ethical considerations are paramount. Organizations must prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability in their data practices, ensuring that data is used responsibly and ethically.
Conclusion
The data landscape in 2025 will be characterized by exponential growth, advanced AI capabilities, and the increasing adoption of cloud computing. These trends present both opportunities and challenges, requiring organizations to adapt and evolve their data strategies. By embracing data governance, investing in data literacy, and prioritizing ethical considerations, we can harness the power of data to drive innovation, solve complex problems, and create a more equitable and sustainable future. As we navigate the complex and evolving data landscape, collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to ethical data practices will be key to unlocking the full potential of this transformative force.