A World On Fire: Warming Trends In 2025 And The Looming Climate Crisis

A World on Fire: Warming Trends in 2025 and the Looming Climate Crisis
The year is 2025. The world is a very different place than it was just a few decades ago. The once-familiar patterns of weather have become erratic, unpredictable, and increasingly extreme. The consequences of our collective inaction on climate change are no longer a distant threat, but a stark reality unfolding before our eyes.
The Numbers Don’t Lie: A Global Fever Chart
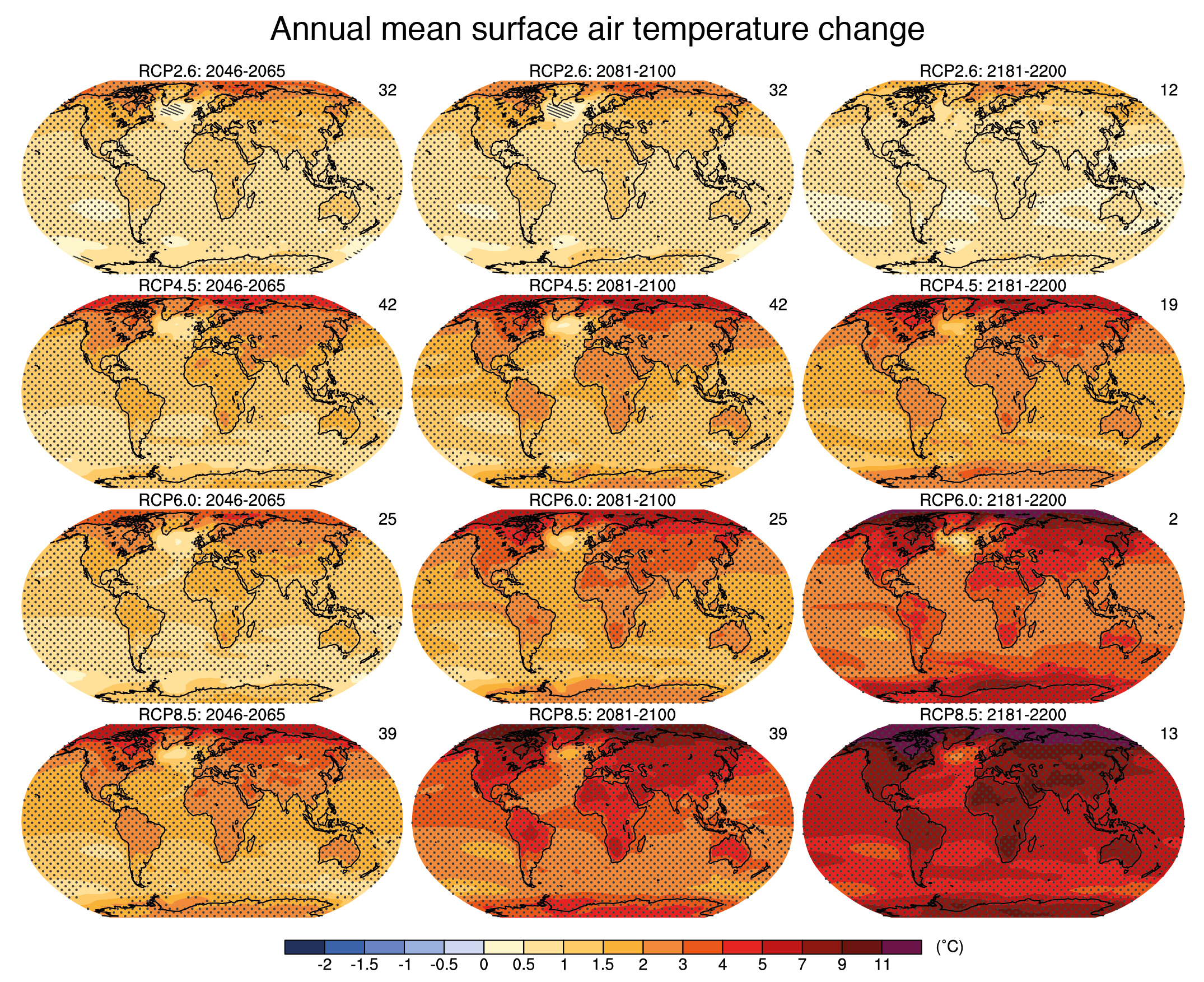
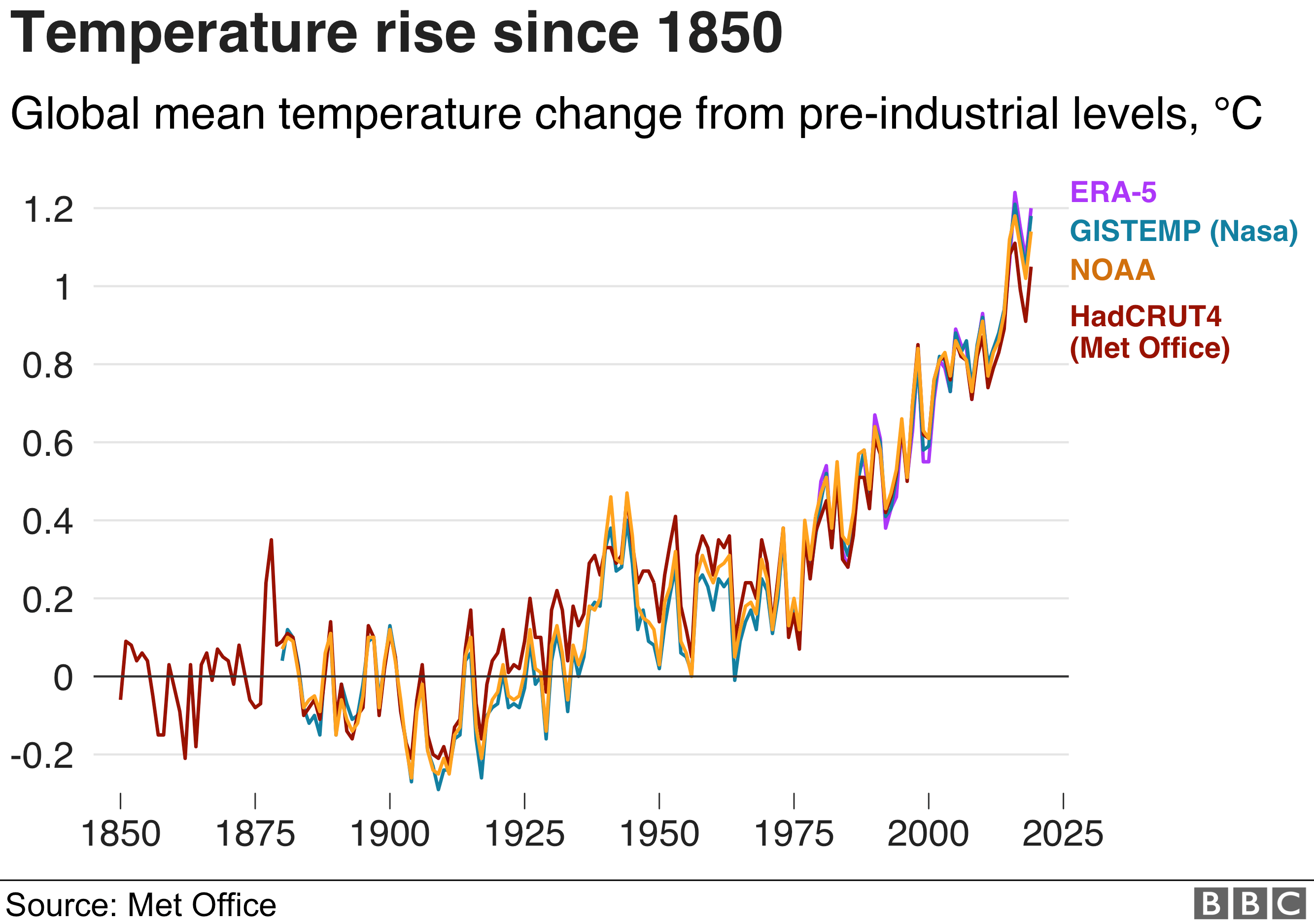
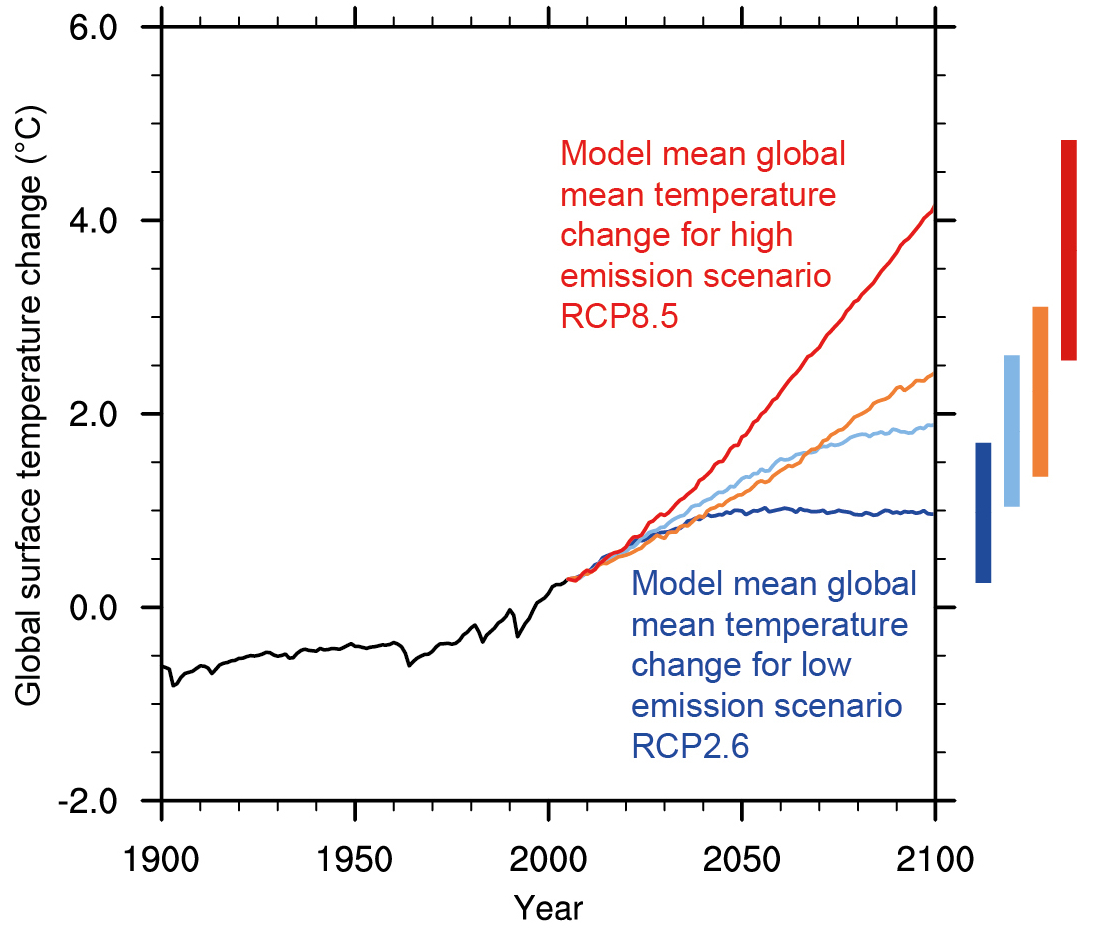
The scientific consensus is clear: the planet is warming at an unprecedented rate. Global average temperatures have risen by over 1 degree Celsius since the pre-industrial era, with the past five years being the hottest on record. 2025, unfortunately, continues this trend.
-
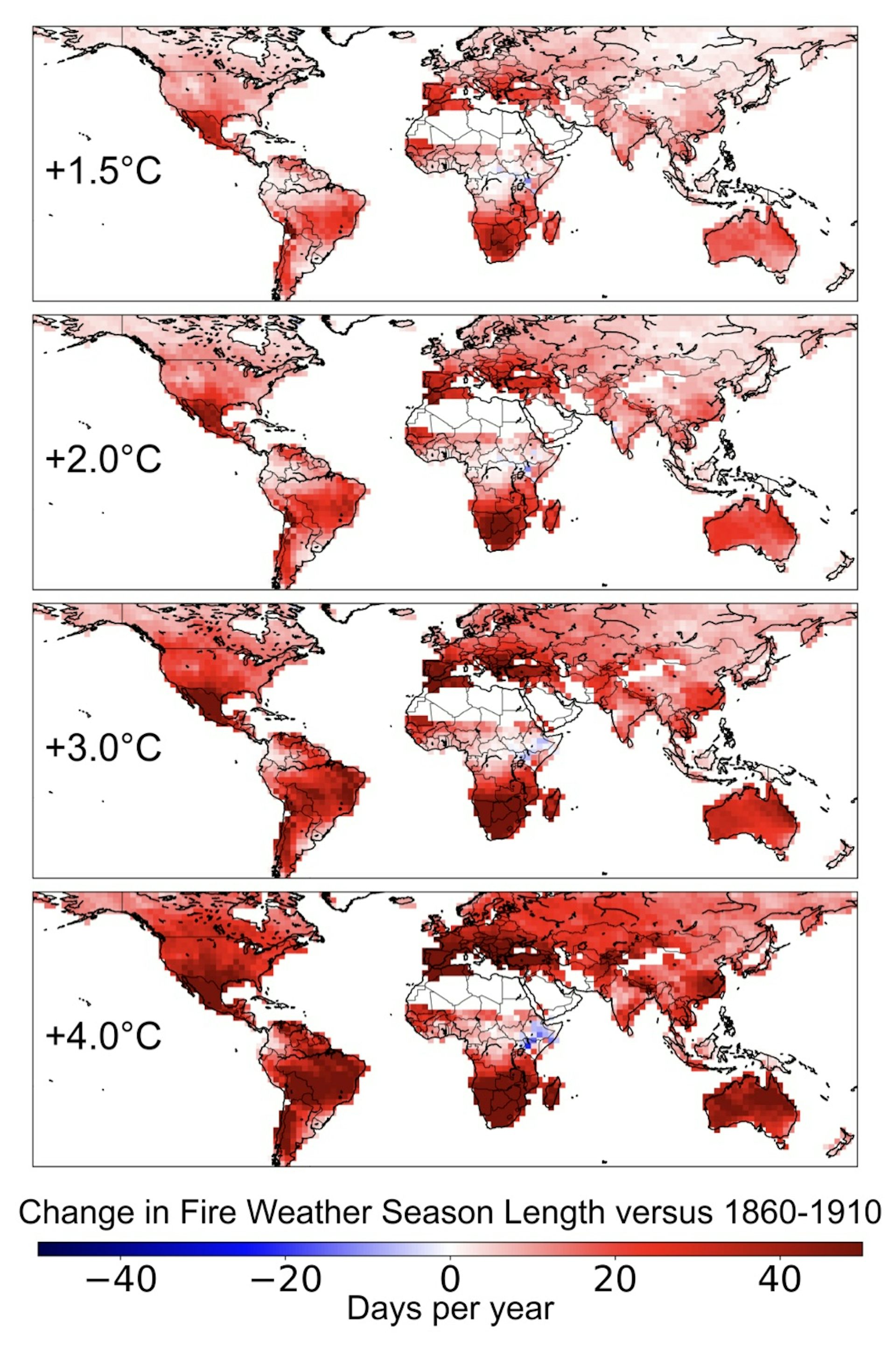
Record-breaking Heatwaves: Summer 2025 witnessed a series of intense heatwaves across the globe, from Europe and North America to parts of Asia and Australia. Temperatures soared to record highs, leading to widespread wildfires, crop failures, and a surge in heat-related illnesses. The Mediterranean region, for example, experienced a prolonged heatwave that lasted for weeks, pushing temperatures well above 40 degrees Celsius, turning once-lush landscapes into parched wastelands.
-
Sea Level Rise: A Rising Tide of Trouble: The relentless melting of glaciers and ice sheets has caused sea levels to rise at an alarming rate. Coastal communities around the world are facing increased flooding, erosion, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources. In 2025, several low-lying islands have been permanently submerged, displacing entire populations and raising concerns about the future of coastal cities. The iconic city of Venice, Italy, is now regularly flooded, highlighting the vulnerability of even developed nations to rising sea levels.
-
Extreme Weather Events: A World of Chaos: The warming climate is fueling more intense and frequent extreme weather events. Hurricanes, typhoons, and cyclones are becoming stronger and more destructive, while droughts and floods are becoming more widespread and severe. The 2025 hurricane season saw a record number of Category 5 storms, causing widespread devastation in the Caribbean and the southeastern United States. Meanwhile, torrential monsoon rains in South Asia led to catastrophic flooding, displacing millions of people and causing widespread damage to infrastructure and agriculture.
Beyond the Numbers: The Human Cost of Climate Change
The impacts of climate change are not just abstract statistics; they are deeply affecting the lives of people around the world. The most vulnerable populations are often the hardest hit, as they lack the resources to adapt to the changing climate.
-
Food Security: A Looming Crisis: Climate change is disrupting agricultural production, making it more difficult to grow food. Droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures are damaging crops and livestock, leading to food shortages and rising prices. In 2025, several regions are experiencing severe food insecurity, with millions of people facing hunger and malnutrition.
-
Water Scarcity: A Thirsty World: As temperatures rise, water evaporates faster, leading to water scarcity in many parts of the world. Droughts are becoming more frequent and severe, putting immense strain on water resources. In 2025, many regions are facing severe water shortages, impacting agriculture, industry, and domestic water supplies.
-
Migration and Displacement: Climate Refugees on the Rise: As climate change intensifies, millions of people are being forced to leave their homes due to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and other climate-related disasters. In 2025, the number of climate refugees is estimated to be in the tens of millions, putting immense pressure on host countries and straining global resources.
A Call to Action: The Time for Solutions is Now
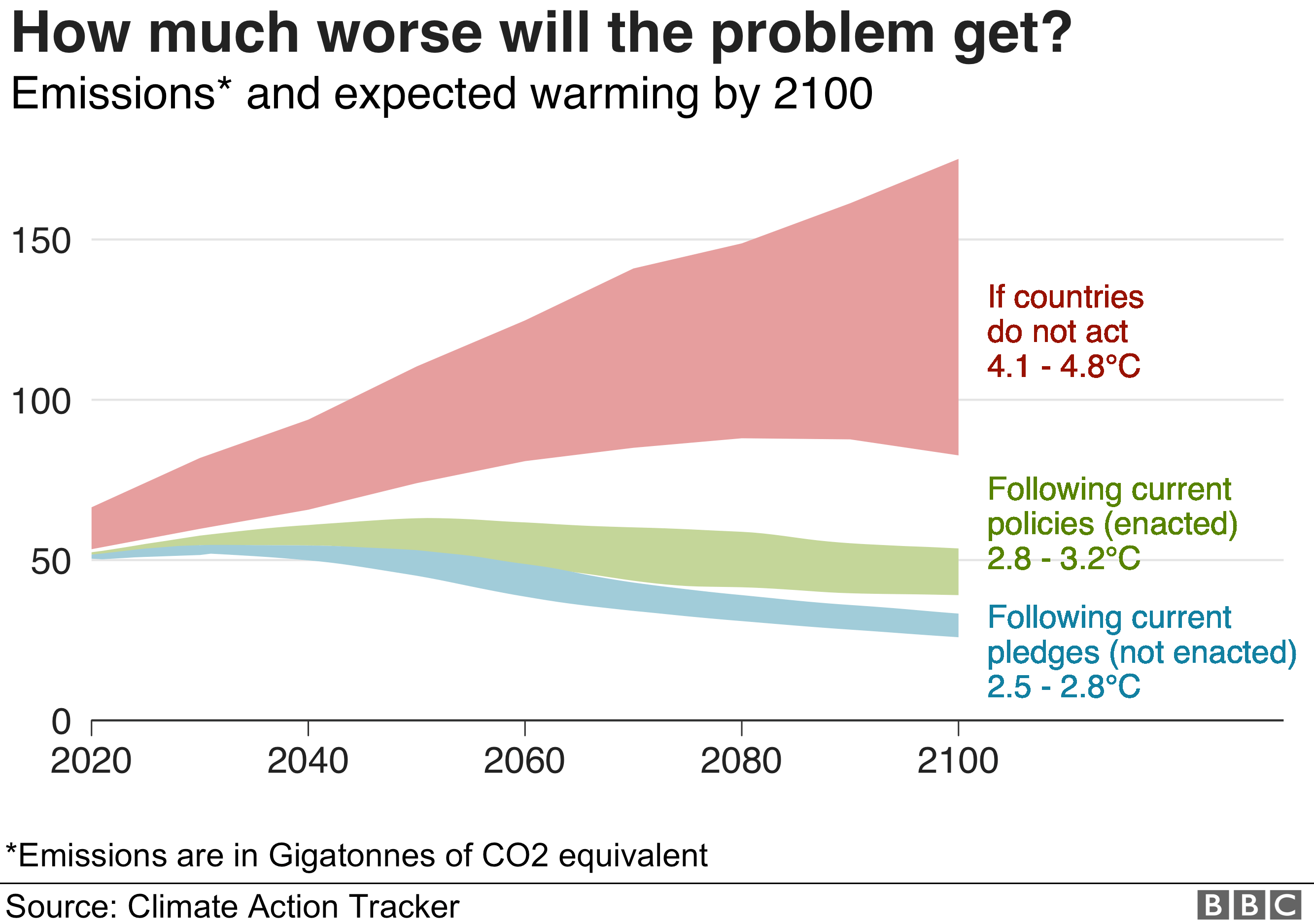
The consequences of climate change are already being felt around the world, and they will only intensify in the years to come. However, all is not lost. There is still time to act, to mitigate the worst impacts of climate change and create a more sustainable future.
-
Transitioning to Renewable Energy: The world must rapidly transition away from fossil fuels and towards clean, renewable sources of energy. Solar, wind, and geothermal power can provide a sustainable and reliable energy source for the future.
-
Investing in Climate Adaptation: Communities must adapt to the changing climate by building resilience to extreme weather events, managing water resources, and protecting coastal areas.
-
Protecting Biodiversity: Climate change is a major threat to biodiversity, as it disrupts ecosystems and drives species to extinction. Protecting and restoring natural ecosystems is crucial for mitigating climate change and preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
-
International Cooperation: Addressing climate change requires global cooperation. Countries must work together to reduce emissions, share knowledge and technology, and support developing countries in their efforts to adapt to climate change.
2025: A Turning Point?
The year 2025 represents a crucial turning point in our collective fight against climate change. The consequences of inaction are becoming increasingly apparent, but so are the opportunities for action. By embracing a global effort to transition to a sustainable future, we can still mitigate the worst impacts of climate change and build a better world for generations to come. The time for denial is over. The time for action is now.